Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
key features will be extracted individually. Since each frame is expected to be
slightly different than the previous frame, our algorithm ensures that the built model
will only include the unique qualities that were constant and consistent throughout
all the used frames; all of the differences should be discarded as noise. Building this
model helps us know what to specifically search for in the future frames, thereby
significantly increasing the speed and robustness of the system.
Skin Color Feature Analysis
The idea of extracting skin color features of the drivers face is to create a user-
specific skin model that can be used as alternative to or as complimentary face/eye
detection and tracking method.
According to [
2
], the chroma components for human skin color using a YCbCr
color model fall into the following ranges:
Cb Range: 77-127
Cr Range: 133-173
This range is purposefully created too broad and too general in order to encompass
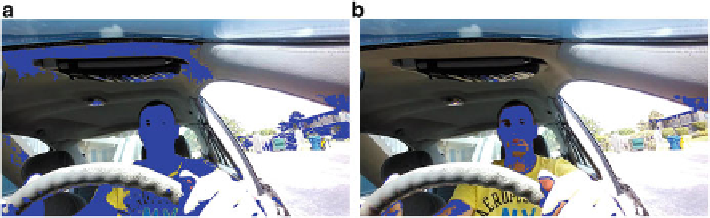
as many skin variations as possible. However, such a broad range does not
compensate for illumination variation and also introduces a large number of false
positives, Fig.
5.4
a clearly shows that—using only these ranges—even though the
face is successfully located, a large number of incorrect detections (e.g. in the t-shirt
area) appeared in the result as well.
Our system overcomes this limitation by extracting the chroma values from the
(previously detected) face pixels and producing a more accurate, user-centric range
for chroma values. This process is computationally inexpensive but can significantly
reduce the number of false positives, as shown in Fig.
5.4
b.
Fig. 5.4
Chroma-based skin detection comparison. (
a
) Generalized skin color chroma range.
(
b
) User-specific skin color chroma range
Search WWH ::

Custom Search