Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
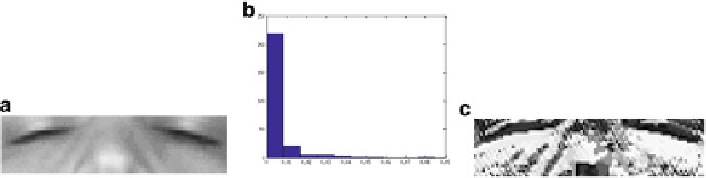
Fig. 4.2
Local Binary Pattern example. (
a
) Raw image. (
b
) LBP histogram. (
c
)LBPimage
A face can be described as a composition of micro-patterns. Every micro-pattern
has its own unique combination of textures which can be well described by LBP.
Therefore, a face can be divided into subsections from which the LBP extraction
can be performed (Fig.
4.2
). LBP histograms can serve as an input vectors to a
classifier.
Eigenfaces
If we take any image of a human face and distort it so that the image
becomes highly noisy, the distorted image will not look completely random and
in spite of the differences between any two distorted images of any face there are
same patterns which occur in them. Such patterns could be the presence of some
objects (eyes, nose, mouth) as well as relative distances between these objects.
These characteristic features are called
eigenfaces
in the facial recognition domain
(Fig.
4.3
). In general, we can treat any object from topological point of view as a
sum of valleys and peaks and their relationships. If we take a face for example,
eyes can be considered to be valleys compared to forehead, nose and cheeks.
A commonly used algorithm for filtering images to emphasize on its topological
structure is the 2D Gabor Function. It can enhance edge contours, as well as valleys
and ridge contours of the image. A Gabor filter is a linear filter used for edge
detection. The frequency and orientation representations of Gabor filters are similar
to those of the human visual system, and they have been found to be particularly
appropriate for texture representation and discrimination. In the spatial domain, a
2D Gabor filter is a Gaussian kernel function modulated by a sinusoidal plane wave.
The Gabor filters are self-similar which means that all filters can be generated from
one mother wavelet by dilation and rotation.
Infrared (IR) Sensitivity
Among the features that are unique only to eyes is the
fact that the eye's pupil reflects almost all of the incoming IR radiation, while the
rest of the human body is absorbing it. This phenomenon can be easily detected
and exploited for face/eye detection purposes in DDD systems equipped with the
appropriate sensors [
3
,
6
,
15
]. In such cases, the reflection of IR light from the pupil
produces a nicely shaped circle, which can be detected using the Circular Hough
Transform [
11
].
Horizontal and Vertical Projection
The summation of grayscale pixel values in
every column/row in an image is called the vertical/horizontal projection. Summed
Search WWH ::

Custom Search