Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
greater than 1, which means it can not give correct answer when there is only one
cluster in the dataset.
This problem is solved by adding a dummy dimension to the original stan-
dardized dataset and clone the original dataset in the space with the dummy di-
mension [33] such that the augmented dataset has at least two clusters. The aug-
mented dataset is denoted as
X
Std
,whichis:
X
Std
=
X
Std
,
0
(5.28)
X
Std
,
d
where
0
is an
N
1 vector with all
elements
d
. They call this method as scale-based with dummy dimension (SBDD)
method.
We can apply the scale-based method on this augmented dataset
X
Std
.Inthis
way, the augmented dataset has at least two clusters. So, we can compare whether
the number of clusters 2 survives in the longest range of the scale parameter or
any other number does. The number of clusters in the original dataset
X
Std
is just
the number of clusters identified in
X
Std
divided by 2.
×
1 zero column vector, and
d
is another
N
×
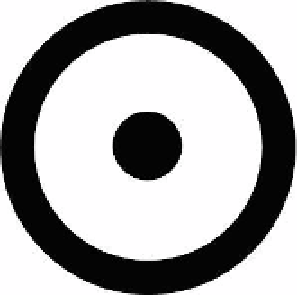
Fig. 5.12.
One cluster encircled by another one.
There is one user-specified parameter
d
in the SBDD method. The value of
d
is suggested to start with a small value of, such as
d
=2. With each value of
d
, the augmented dataset is constructed by Eq. 5.28. Scale-based method is ap-
plied on
X
Std
. If the scale-based method identifies clusters whose centers have the
following pattern:
(
x
1
,
0)
,
(
x
2
,
0)
,...,
(
x
K
,
0)
(
x
1
,
d
)
,
(
x
2
,
d
)
,...,
(
x
K
,
d
)
(5.29)
the SBDD algorithm stops. Otherwise, increase
d
by a step size such as ∆
d
=0
.
5.








Search WWH ::

Custom Search