Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
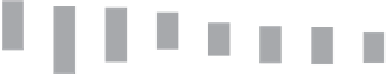
Danish Energy Related CO2 Emissions
70 000
64 294
60 277
60 000
53 591
53 117
50 827
50 927
49 384
48 981
50 000
40 000
30 000
20 000
10 000
-
1980
1990
1995
2000
2005
2008
2009
2010
Figure 4.1
. CO
2
Emissions Trends in Denmark
Source
: Danish Energy Agency. 2011.
Annual Energy Statistics 2010
. Copenhagen: Danish Energy Agency.
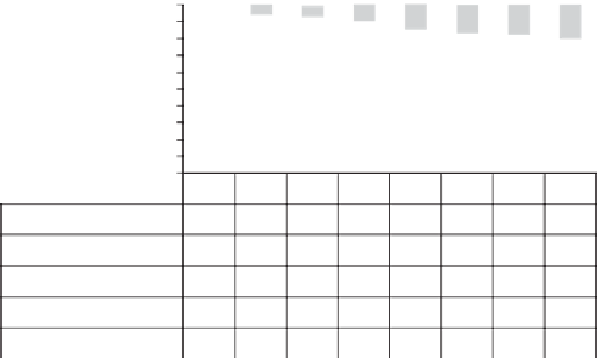
100.0
90.0
80.0
70.0
60.0
50.0
40.0
30.0
20.0
10.0
0.0
1980
1990
1995
2000
2005
2008
2009
2010
Renewable energy
2.9
6.1
7.0
9.8
14.7
16.7
17.8
20.2
Waste, nonrenewable
0.4
0.7
1.1
1.6
1.9
2.0
2.0
1.8
Coal and coke
29.6
39.9
31.5
20.9
19.5
21.6
21.1
18.0
Natural gas
0.0
10.0
15.9
22.9
22.6
20.5
20.4
21.8
Oil
67.1
43.3
44.5
44.8
41.4
39.2
38.7
38.1
Renewable energy
Waste, nonrenewable
Coal and coke
Natural gas
Oil
Figure 4.2
. Primary Energy Consumption by Fuel Source (in %)
Source
: Danish Energy Agency. 2011.
Annual Energy Statistics 2010
. Copenhagen: Danish Energy Agency.
communities, and consumers to reduce Denmark's sizable carbon footprint
through energy eiciency improvements.
Energy eiciency improvement tells only part of the story in Denmark's
energy sector. In 2010, CO
2
emissions were 23% lower than 1980 levels and
7% lower than 1990 levels. As Figure 4.1 illustrates, Denmark's CO
2
emis-
sions reached a peak in 1995 before beginning a progressive decline.
As Figure 4.2 suggests, the diminishing role of oil in Denmark's primary
energy mix explains part of the nation's progress in reducing CO
2
emissions.