Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
By the way, both of these compounds are chlorinated. As mentioned, special
precautions must be taken when dealing with such halogenated compounds, since
even more toxic compounds than those being treated can end up being generated.
Incomplete reactions are very important sources of environmental contaminants.
For example, these reactions generate products of incomplete combustion, such
as dioxins, furans, carbon monoxide, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and hex-
achlorobenzene. Thus, whether a system is classified as green, at least in the case
of treatment, is quantifiable.
Formation of Unintended By-products
One of the major incentives for pollution prevention is that with some amount
of forethought we should be able to avoid the creation of toxic by-products. If we
choose a production cycle that greatly reduces the creation of toxic substances or
that generates a different, less toxic by-product, we have avoided undue costs, legal
problems, and risks down the road. This can be demonstrated by the troublesome
and downright scary pollutant, dioxin.
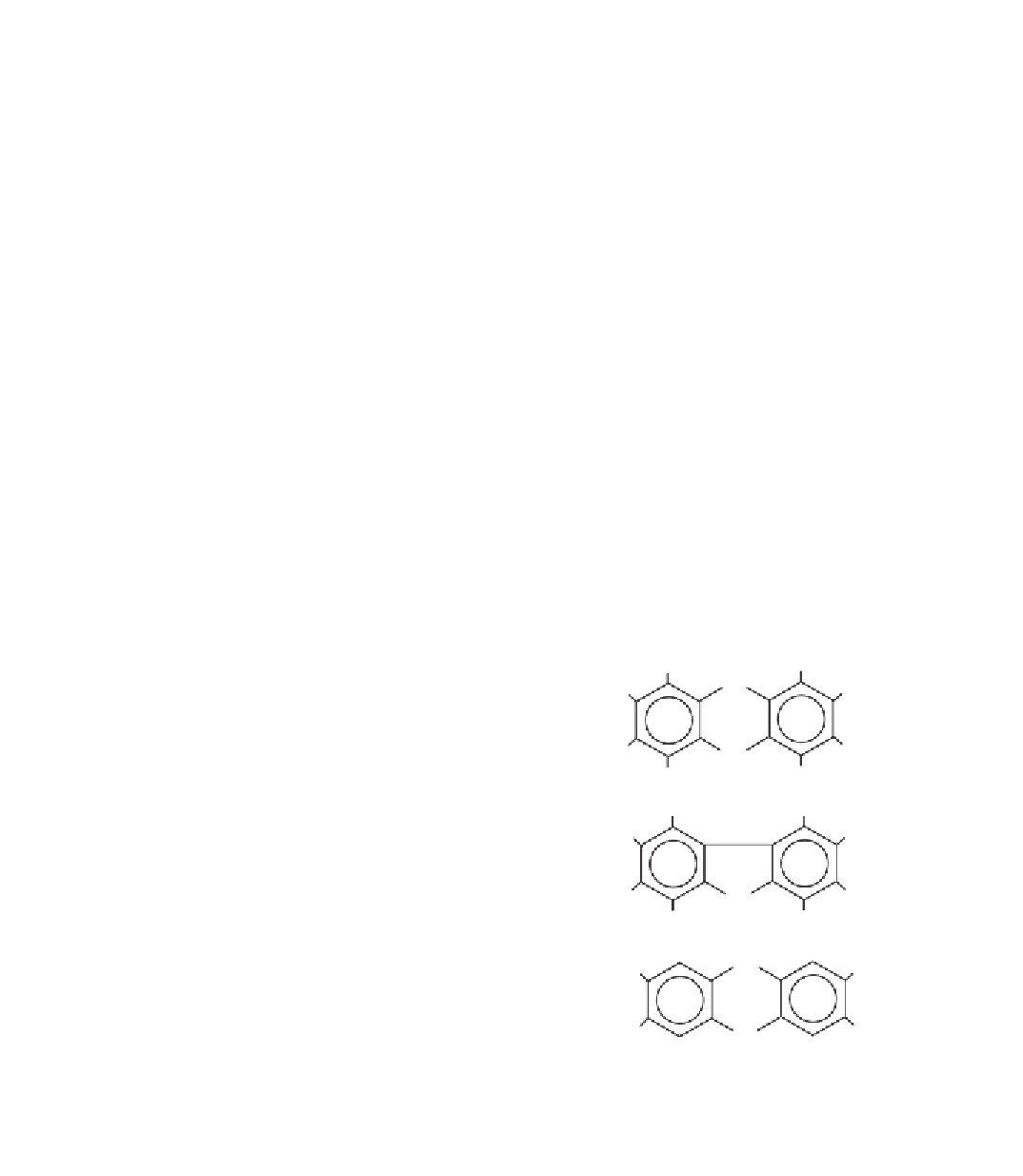
Chlorinated dioxins have 75 different forms and there are 135 different chlo-
rinated furans, simply by the number and arrangement of chlorine atoms on
the molecules. The compounds can be separated into groups that have the same
number of chlorine atoms attached to the furan or dioxin ring. Each form varies
in its chemical, physical, and toxicological characteristics (see Fig. 3.11).
Figure 3.11
Molecular
structures of dioxins and furans.
Bottom structure is of the most
toxic dioxin congener,
tetrachlorodibenzo-
para-
dioxin,
formed by the substitution of
chlorine for hydrogen atoms at
positions 2, 3, 7, and 8 on the
molecule.
9
1
O
2
8
3
7
O
4
6
Dioxin structure
9
1
8
2
7
O
3
4
6
Furan structure
O
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
O
2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-
para
-dioxin
Search WWH ::

Custom Search