Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
and the new graph has the form
and the IM
G
∗
can be reduced to
2
1
3
1
2
3
1
1
d
,
3
,
8
e
,
4
,
4
g
,
5
,
5
h
,
5
,
5
1
1
3
1
1
1
a
,
2
,
3
4
,
5
2
,
4
0
,
1
0
,
1
1
1
2
b
,
3
,
3
3
,
0
0
,
1
0
,
1
0
,
1
1
1
c
,
3
,
2
0
,
1
0
,
1
0
,
1
0
,
1
2
1
3
1
d
,
3
,
8
0
,
1
0
,
1
4
,
5
0
,
1
3
1
2
1
e
,
4
,
4
0
,
1
0
,
1
3
,
6
0
,
1
1
7
1
1
f
,
10
,
8
0
,
1
0
,
1
0
,
1
3
,
4
2
3
3
1
,
5
,
5
,
,
,
5
,
5
g
0
1
0
1
0
1
Obviously, vertex
f
remains in the first index set, because an arc goes out of it.
On the other hand, vertex
c
here is an isolated one.
The present text was written in the end of 2013 and it was published in [19], when
I, as an Editor-in-Chief of the journal “Notes on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets”, received
(in March 2014) the paper of Parvathi Rangasamy [45] that contains very similar
ideas. My paper was published in No. 1 for 2014 and Parvathi's paper in No. 2 of
the above mentioned journal.




































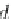
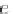












Search WWH ::

Custom Search