Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
individual heterogeneity in catchability. Nevertheless, given the difficulty of esti-
mating abundance by any other means in this case, this approach could be useful
as a last resort, so long as the likely bias is understood and consequent uncertainty
acknowledged.
Fitted
Fitted
Squared
Week
Catch
Effort
CPUE
population
catch
deviation
ˆ
ˆ
(
C
ˆ
)
2
t
C
E
C/E
1
39
108
0.36
303
41.12
4.49
2
46
117
0.39
264
38.81
51.73
3
29
127
0.23
218
34.78
33.38
4
23
89
0.26
189
21.13
3.51
5
24
104
0.23
166
21.68
5.39
6
20
68
0.29
142
12.12
62.06
7
3
95
0.03
122
14.55
133.31
8
9
87
0.10
119
12.99
15.94
9
12
91
0.13
110
12.56
0.31
10
10
93
0.11
98
11.43
2.05
11
14
109
0.13
88
12.03
3.88
12
11
115
0.10
74
10.67
0.11
13
5
66
0.08
63
5.21
0.04
14
11
59
0.19
58
4.29
45.09
15
9
74
0.12
47
4.35
21.61
16
1
72
0.01
38
3.42
5.85
Total
Sum of
catch:
266
squares:
388.77
(observed: ; fitted:
)
Effort (o)
(observed: ; fitted:
)
(a)
(b)
Catch
80
0.4
120
60
0.3
80
40
0.2
40
20
0.1
0
0
0
0
5
10
15
0
0
5
10
15
Week
Week
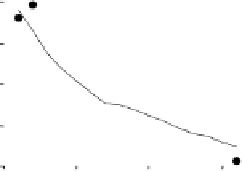
Fig. 2.8
Change in (a) catch and effort, and (b) catch per unit effort over
time, during the cull of wild pigs in Great Smokey Mountain National Park.
Source
:
Lancia
et al
. (1996)
.