Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
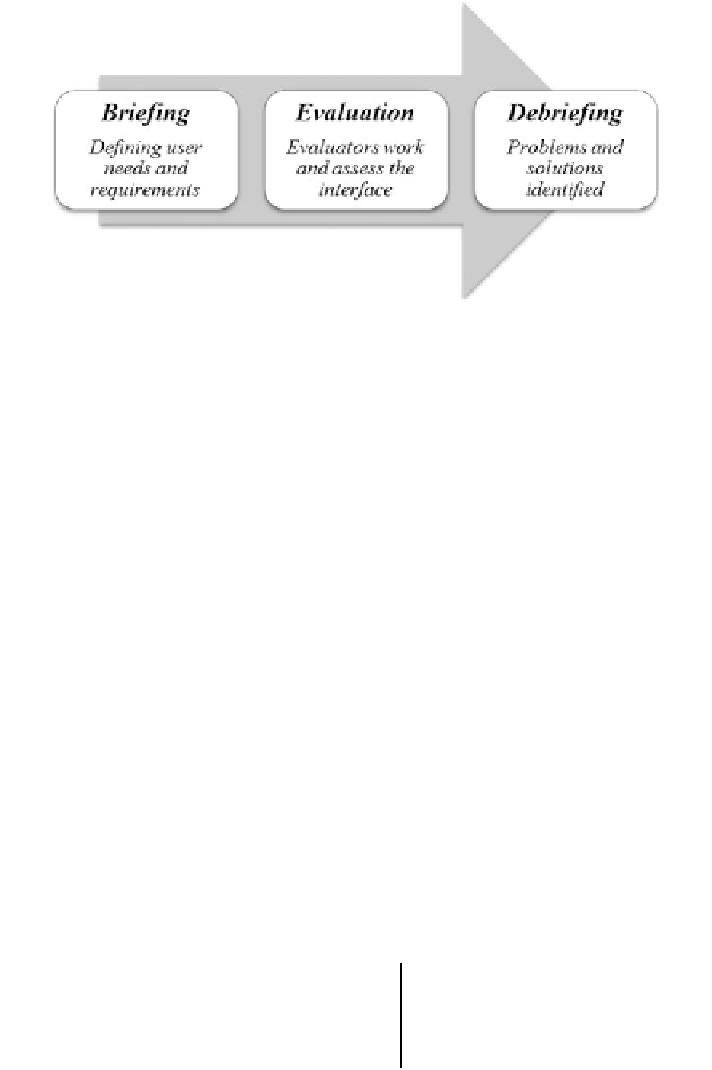
Fig. 5.2 Basic process of heuristic evaluation
5.5 Goals, Operators, Methods, and Selection Rules
(GOMS)
GOMS model was developed and invented by Card et al. (
1983
). This model aims
to present the knowledge of determined human computer interaction and how user
can interact with computers and the implications for designers. This model
endeavors to reduce the complexity in the interface as well as in the cognitive
resources and engineering. Under this model,
there are speci
c elements that
describe purposeful HCI, illustrated in Table
5.1
.
Goals specify what the user wants and intend to achieve.
Operators are the building blocks for describing human
computer interaction at
-
the concrete level.
Methods are sequences of sub-goals and operators to accomplish a goal.
Selection rules predict which method will be used. For example,
“
If the mouse is
working, select
'
point to an item on screen,
'
if not select choose OPEN option in
file menu.
”
Finally, GOMS model is based on levels of interaction that bridge the gap
between the abstract (psychological) task and the concrete (Physical System).
Table 5.1 GOMS
Goals
User needs
Operators
HCI building blocks
Methods
Programs built through operators
Selection rules
De
nition of what methods will be used




Search WWH ::

Custom Search