Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
follows the stage of implementation of the product. Conceptual design involves the
creation of a conceptual model of the Web site that produces a set of classes,
subsystems, and their relationships. Navigational design implies the description and
visualizations of the navigational structure of the Web site, through varied navi-
gational classes such as nodes, links, indexes, and tours. The abstract interface
design then interprets the conceptual model and the navigational structure into
interface classes
fields, buttons, etc. Throughout the entire design process,
OOHDM uses object-oriented modeling as its main tool, hence its name (Schwabe
et al.
1999
). It is ultimately a methodology that aims at helping developers and
designers create single-user hypermedia environments, but researchers have
observed that it is not adequate to projects that want to embed authoring functions
in the Web site or application, permitting users to edit and add content (Sch
—
text
ü
mmer
et al.
1999
).
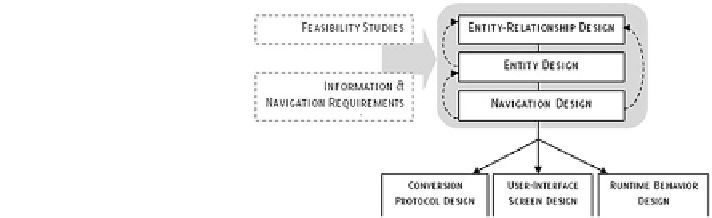
Similarly, the relationship management methodology (RMM) focused on hy-
permedia applications, as the vehicle for the relationships between objects.
Developed by Isakowitz et al. (
1995
), it is a structured, step-by-step methodology.
The process starts with rigorous analysis of the Web site
s objectives, the market,
and the user base, as well as information sources, permissions, distribution chan-
nels, and other business-related principles. Then, much like the OODHM, the
design process is broken apart,
'
in this case,
in six stages related to different
dimensions of design, as outlined in Fig.
1.4
.
While OOHDM and RMM are adaptations of traditional, rigid IS development
methodologies, other methodologies have attempted to bring a more holistic
approach to Web development, in accordance with the large scope of goals and
needs of Web projects. The Web information system development methodology
(WISDM) was developed by Vidgen et al. (
2002
) in an attempt to combine essential
principles of the Multiview IS development methodology with the speci
c char-
acteristics of Web projects. Multiview is a contingent, goal-oriented solution to the
development of IS projects with complex and diffuse needs and requirements.
Likewise, WISDM posits that a uni
ed approach that brings together the different
levels of the development project, proposing a socio-technical approach. The
development process is broken apart into a four-stage framework. The analysis
stage is divided into organizational analysis (where goals of the Web project are
integrated into the organization
'
s general strategy) and information analysis (where
Fig. 1.4 Design processes of
the RMM (adapted from
Isakowitz et al.
1995
)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search