Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
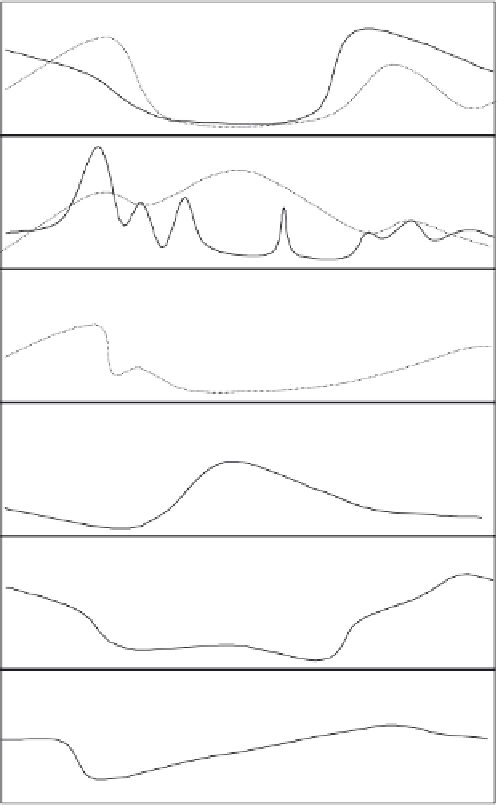
Light at stream surface
Leaves in stream
Discharge
Temperature
Periphyton
Fast seasonal, insect larvae with summer reproduction
Slow seasonal, insect larvae with winter growth
Long-lived species and quick reproducers
(fish, predators, mosses , FBOM feeders)
Winter
Spring Summer
Autumn Winter
FIGURE 20.7
A hypothetical seasonal successional sequence in a small temperate stream in
a deciduous forest.
green algae take more time to establish. Finally, cyanobacteria dominate as
nitrogen becomes limiting. The successional patterns discussed here pro-
vide generalized and simplified models, to which exceptions clearly exist,
mainly to illustrate the potential for seasonal succession in streams.
Indirect Interactions
Indirect interactions are interactions between two species mediated by
one or more other species (Wootton, 1994). One of the strongest examples
of this is the trophic cascade, in which changes in the abundance of a top
predator can alter the abundance of primary producers as mediated by in-
teractions among several other species. Here, I discuss indirect interactions
in a general sense.

Search WWH ::

Custom Search