Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
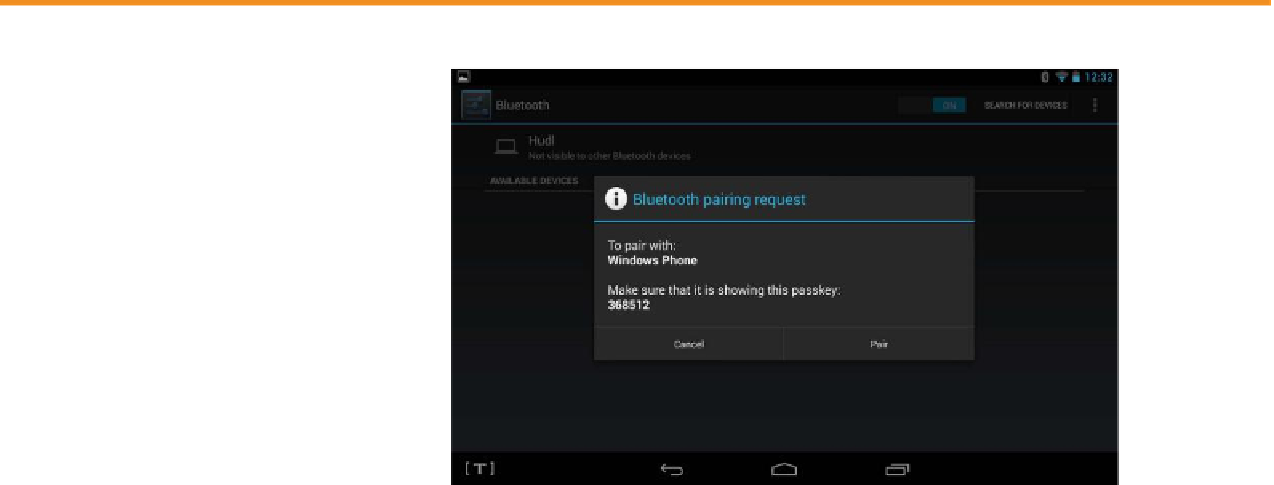
Pairing Bluetooth Devices
To connect devices via Bluetooth,
you must pair them. Pairing can
take several different forms,
depending on the devices. For
example, one device might gener-
ate a PIN code, and the other one
might prompt you to type that PIN
code to confirm. Obviously, that
works only if both devices have
a display screen on which a PIN
code could display. For a device
without a display, such as a
Bluetooth mouse, the device will
have a button you can press to
make it temporarily discoverable.
Press the button (you may have
to hold it for a few seconds),
following the directions in the
device's documentation to make it discoverable, and then select it on the screen of the device with which you want
to pair it. In Windows, you can access the Bluetooth controls via the Control Panel.
Infrared
Infrared
technology uses light waves to “beam” information from device
to device. Infrared was the method of choice for connecting wireless
peripherals a decade or so ago, but Bluetooth has mainly superseded it
today. However, infrared is still used for most remote controls for TVs and
other home theater components. The main drawback of infrared trans-
mission is that it must have a clear line of sight between the two points.
The standard for an infrared connection is IrDA (short for Infrared Data
Association, the organization that created and manages the standard).
infrared
Older type of wireless communication
that used light waves to pass simple information
between nearby devices.
Microwave
Microwaves are high-frequency radio waves. A
microwave communica-
tion system
allows two locations to be wirelessly connected by using a
high-frequency communication band, much higher than that used for
Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. The points can be miles apart (up to about 25 miles),
but as long as there are no visible obstructions between them, they can
exchange data. Because line of sight is so critical for microwave communi-
cations, the transmitters are often placed high up on towers or buildings.
Microwave technology is not as widely used today as it was prior to the
development of satellite networking systems, but it still has some special
uses; for example, military forces use it to quickly set up communications
in areas where the terrain is too rugged to support wired connections and
security is critical. (A point-to-point microwave connection is more secure
than a connection that goes through a satellite.)
microwave communication system
A
secure, point-to-point wireless networking technol-
ogy that requires a line of sight between the two
points.
Quick Review
1
What is the difference between a LAN and a WAN?
2
Name three different wireless networking technologies.
3
What is a client/server network?