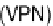Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Private Digital Networks
Many companies maintain high-speed connections between their loca-
tions. They can do so by leasing a line, running their own cables, or
using the existing pathways of the Internet. Using the Internet is the
most cost-effective method, but not the most reliable method, because
the connection can be affected by Internet traffic problems and connec-
tions that other companies control and maintain.
Using the Internet is also not very secure; it's an open system and data
being sent and received can easily be snooped. To tighten the security
when using the Internet as a conduit, many companies use a software
technology called
virtual private networking (VPN)
. VPN technol-
ogy creates a secure, tamper-resistant data tunnel between two points
on the Internet, so that sensitive information can be exchanged securely,
as in Figure 8.1. A VPN allows an employee who is working outside of
the company's main building to connect to any of the internal network
resources, just as if he or she were in the building.
virtual private networking (VPN)
A method
of creating a secure, private communication tunnel
using a public communications channel such as
the Internet.
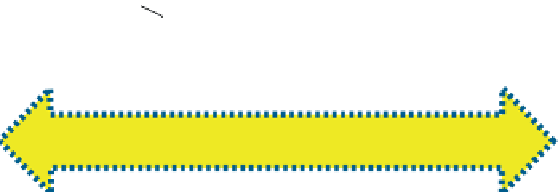
Figure.8 1
A VPN creates a secure connection between two points using the Internet's
infrastructure to physically carry the data.
Satellite Data Networks
A
satellite
is a transmitter/receiver unit that orbits the Earth, more
than 22,000 miles up. Satellites are in geosynchronous orbit (that is,
their orbit is synchronized with the Earth's orbit), so they do not appear
to change in position compared to any location on Earth. A satellite
contains transponders, which are two-way radios that communicate with
stations on the ground. Satellites are used to quickly send information
between two points on Earth that are physically separated by a great dis-
tance. For example, when the Olympics are held in one country, satellites
are used to broadcast the video of each competition nearly instantly to
every other country. Satellites are also used for services like satellite radio
(Sirius/XM, for example) and satellite TV broadcasts such as DirecTV
and Dish Network (see Figure 8.2). Some Internet services also use satel-
lites to provide Internet access to areas where other high-speed connec-
tion technologies are not available.
satellite
A data transmitter/receiver in geosyn-
chronous orbit with the Earth.