Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
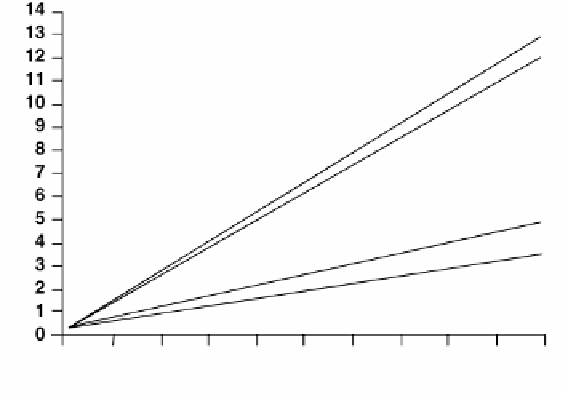
Figure 3.4
Carboxyhemoglobin levels in human blood as a function of exposure
duration. (From USEPA,
EPA/600/8-90/045f
, 1991.)
tion, many more cases associated with sublethal exposures occur over a
broad range of concentrations (30 to several 100 ppmv). Under these expo-
sure conditions, individuals may experience a variety of central nervous
system symptoms which are dose dependent. These may include, at rela-
tively low concentrations (40 to 60 ppmv), headache and low levels of
fatigue, and, at higher concentrations (75 to 200 ppmv), nausea, vomiting,
and sleepiness.
The major immediate effect of CO is to chemically bond with hemoglobin
in the blood to form carboxyhemoglobin (COHb). Carbon monoxide com-
petes with oxygen (O
2
) for hemoglobin binding sites, with an affinity for
hemoglobin that is 200 times greater than that of O
2
. Because it competes with
O
2
for hemoglobin and is more tightly bound to it, CO can significantly reduce
the amount of O
2
transported to body tissues. It also binds to intracellular
proteins such as myoglobin, cytochrome oxidase, tryptophan oxidase, and
dopamine hydroxylase. Such binding may cause extravascular effects.
Because brain tissue is very sensitive to changes in O
2
availability, it
responds relatively quickly to diminished O
2
supplies associated with CO
exposures. As a consequence, central nervous system-type effects are asso-
ciated with CO exposures.
Exposure to CO can be determined by measurement of COHb in blood.
This is usually <1% for individuals not exposed to CO. Among cigarette
smokers, COHb concentrations vary from 3 to 8%. Blood COHb levels asso-
ciated with different CO concentrations, durations, and breathing rates are
illustrated in
Figure 3.4
.
At the Occupational Safety and Health Administra-
tion's (OSHA) permissible exposure limit (PEL) of 50 ppmv 8-hour time-
weighted average (TWA), an individual would have approximately 5% of
his/her hemoglobin bound as COHb; at 100 ppmv it would be over 10%.