Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.3 Key Issues that are Influenced by Global Warming
The key changes to the terrestrial and aquatic environments in response to global
warming can be distinguished as: (i) increase of global average air and water tem-
peratures (Fig.
2
) (IPCC
2007a
). Global surface temperatures have increased by
0.74 ºC since the late nineteenth century, and 11 out of the 12 warmest years on
record have occurred since 1995 (IPCC
2007a
).The temperature increase is wide-
spread over the globe and is higher at higher northern latitudes. Indeed, average
Arctic temperatures have increased at almost twice the global average rate in the
past 100 years (IPCC
2007a
). (ii) Decreases in snow cover and in the Northern
Hemisphere sea ice extent. The result is a shorter freezing season for lakes, rivers
and sea ice (Fig.
2
) (IPCC
2007a
). Since 1978, satellite data have been showing
that the annual average Arctic sea ice extent has shrunk by 2.7 % (2.1-3.3 %) per
(a)
(b)
(c)
Year
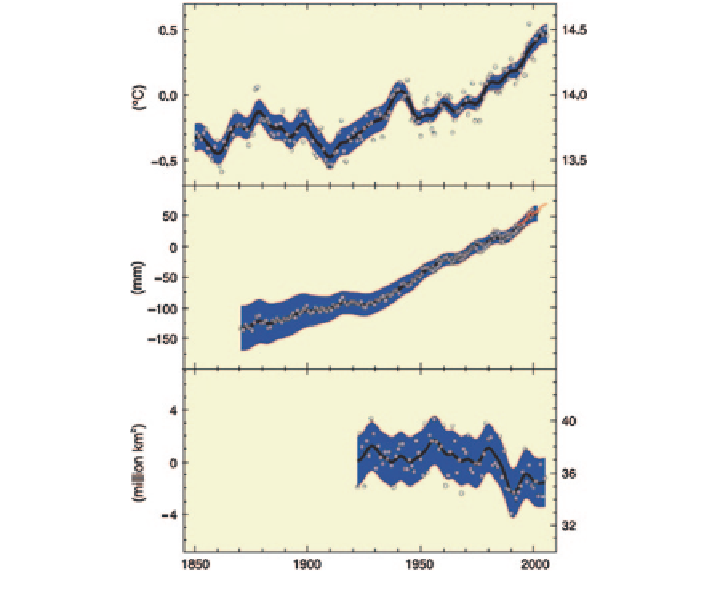
Fig. 2
Observed changes in
a
global average surface temperature;
b
global average sea level
from tide gauge (
blue
) and satellite (
red
) data; and
c
Northern Hemisphere snow cover for
March-April. All differences are relative to corresponding averages for the period 1961-1990.
Smoothed curves represent decadal averaged values while circles show yearly values. The shaded
areas are the uncertainty intervals estimated from a comprehensive analysis of known uncertain-
ties (
a
and
b
) and from the time series (
c
).
Data source
IPCC (
2007a
)