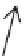Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
in seawater samples as well as standard samples suggests that the fluorescence of
tryptophan is approximately four times higher than that of tyrosine (Yamashita and
Tanoue
2003a
; Mostofa KMG and Sakugawa LH, unpublished data). The molec-
ular formula of tyrosine is C
9
H
11
NO
3
and its molecular weight is 181.19. The
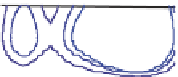
different chemical structure of tyrosine compared to tryptophan (Fig.
3
t) could
account for its much lower fluorescence intensity (Yamashita and Tanoue
2003a
;
Mostofa KMG et al., unpublished data).
Phenylalanine shows two fluorescence peaks at Ex/Em
=
255-265/284-
286 nm (peak T-region) and at Ex/Em
=
~ 220/284-286 nm (peak T
UV
T-region) in
marine waters and in standards dissolved in Milli-Q or seawater (Fig.
3
u; Tables
1
,
2
). The phenylalanine-like component has been identified at Ex/Em
=
260/286 nm
for a phenylalanine standard dissolved in Milli-Q water, and at 260/284 nm for a
phenylalanine standard dissolved in sea water; at 255-265/284-285 nm in marine
waters; and at 265/306 nm in ice samples from the Antarctic and Arctic Ocean
(Yamashita and Tanoue
2003a
; Nakajima
2006
; Dubnick et al.
2010
). The molec-
ular formula of phenylalanine is C
9
H
11
NO
2
and its molecular weight is 165.19.
The absence of the OH group in the benzene ring of phenylalanine (Fig.
3
v) can
account for the reduced fluorescence intensity when compared to tyrosine, and for
the presence of fluorescence excitation-emission maxima at shorter wavelength
regions than for tyrosine or tryptophan.
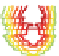
(u)
(v)
400
365
330
Peak T
295
260
235
Peak T
UV
250 300 350 400 450 500
Em wavelength (nm)
450
450
400
400
Peak A
Peak W
350
350
(w)
(x)
300
300
250
300
350
250
300
350
The molecular structure of tyrosine (
t
).
u
,
v
The fluorescent EEM spectra of standard phenylalanine
amino acid (
u
) dissolved in Milli-Q waters (
Data source
Nakajima
2006
). The molecular structure of
phenylalanine (
v
). The fluorescent components of standard DSBP (
w
) in its aqueous samples and in
downstream waters (
x
Kurose River, Japan) identified using PARAFAC modeling on their respective
EEM data (
Data source
Mostofa and Sakugawa
2009
).