Geography Reference
In-Depth Information
are viewed in terms of proximal relationships, and masts are resolved so
each area is represented once. For example, if we have the taxon-area
cladogram AB (C (D, E)), resolving mast AB implies that two area clado-
grams are obtained: A (C (D, E)) and B (C (D, E)), which together result in
AB (C (D, E)). Ebach et al. (2005a) suggested that the transparent method
should be implemented before the paralogy-free subtree analysis.
Redundant Distributions
Alsoknownasareasofsympatry(Enghoff1996),
redundant distributions occur when an area appears more than once in a
taxon-area cladogram because in this area, two or more terminal species
are distributed. In the taxon (1 (2 (3 (4, 5)))), if species 1 and 5 are distrib-
uted in North America when the species are replaced by the areas, this area
stitute a monophyletic group, obtaining a resolved area cladogram is simple.
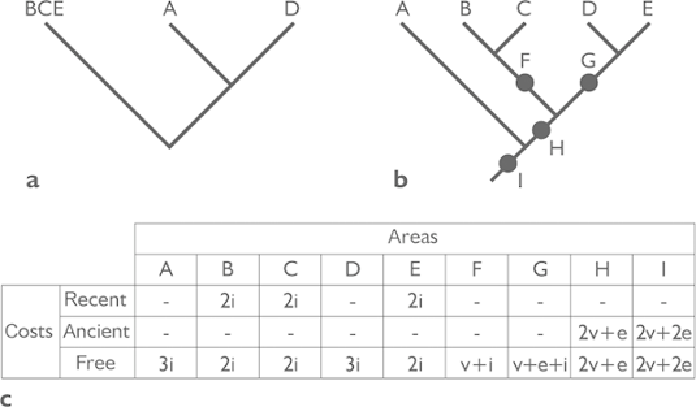
Figure 5.4
Resolution of a widespread taxon under the event-based approach. (a)
Taxon-area cladogram with a taxon widespread on areas B, C, and E; (b) general
area cladogram; (c) costs of each area under the recent, ancient, and free options.
e, extinctions; i, dispersal; v, vicariance.