Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3.2.2 Air Changes and Thermal Building Performance
Air exchange rates were measured in the Lamparter building using a tracer gas unit
from Dantec (Vivo Dosing 20H31 and Vivo TriGas 20T34). The three-channel mea-
surement unit measures SF
6
concentrations in three different locations within a room.
Only if all three concentrations are similar is the air exchange calculated from the
concentration drop.
The air change rates measured during 170 night hours in summer 2003 gave an
average of 9
.
3h
−
1
at an average wind speed of 1
.
1ms
−
1
. The wind direction was
between east and south for 90% of all measurements with decreasing speed over the
course of the night.
There was an increase of air change
n
with wind speed
v
following a linear correla-
tion with a very weak correlation coefficient of 0.1 (see Figure 3.8), but no measurable
increase of air change with temperature difference between the inside and outside air:
=
+
n
1
.
8173
v
7
.
2544
The analysis of air flow within the building using artificial fog showed that the
air exchange was largely wind induced and that the thermal buoyancy effect was
especially small in the first-floor offices. The neutral zone within the two-storey build-
ing is at the top of the first floor and the driving pressure for buoyancy is therefore
small.
During daytime with the mechanical ventilation system in operation, the flow
velocity measured below the north-east office ceiling was quite constant at 0
.
15
±
0
.
02 m s
−
1
. Higher wind speeds or wind blowing directly on the north-eastern fa¸ade
only marginally increased the air velocities. At night with only passive ventilation the
flow velocity dropped to 0
.
01m s
−
1
if the windows were closed. When the windows
are open, the wind direction is the decisive parameter. If the wind is from northern
directions, the air velocities at the ceiling are between 0.2 and 0
.
3ms
−
1
even at low
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
wind speed / m s
-1
Figure 3.8
Air changes as a function of wind speed










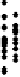
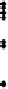
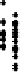
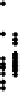





























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search