Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
EXAM TIP
Secondary zones are a seductive solution to many situations, but they have some limita-
tions that exam question writers are likely to take advantage of. One is that they present a
potential security consideration because the entire zone is available, so be leery of ques-
tions that include security as a called-out concern where a secondary zone appears to be
the answer. the other limitation is that they can't be active Directory-replicated because
they can't be stored in active Directory. Secondary zones are always file-based zones.
Zone and conditional forwarder storage is usually set at creation time, but you have the
option to change it after the fact by using either the DNS Management console. To configure
an existing conditional forwarder that is not stored in Active Directory to one that is, use the
DNS Management console (the operation is not supported in Windows PowerShell). The same
is true for converting a file-based DNS zone into an Active Directory-integrated one. Use the
DNS Management console.
So to convert a DNS file-based stub zone into an Active Directory-integrated one, follow
these steps:
Open the DNS Manager console.
1.
Expand the server on which you are converting the stub zone.
2.
Select the stub zone folder in the console tree and right-click.
3.
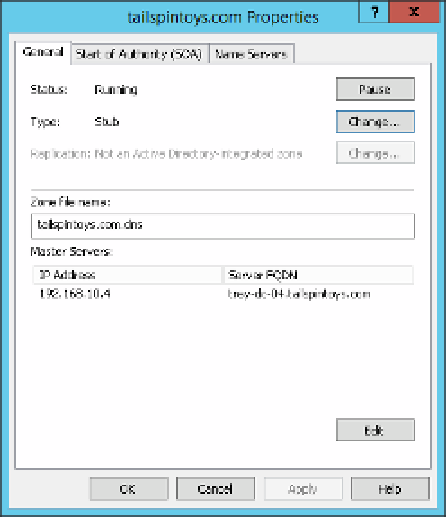
Select Properties from the menu to open the Zone Properties dialog box shown in
Figure 3-9.
4.
FIGURE 3-9
The Zone Properties dialog box for tailspintoys.com