Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
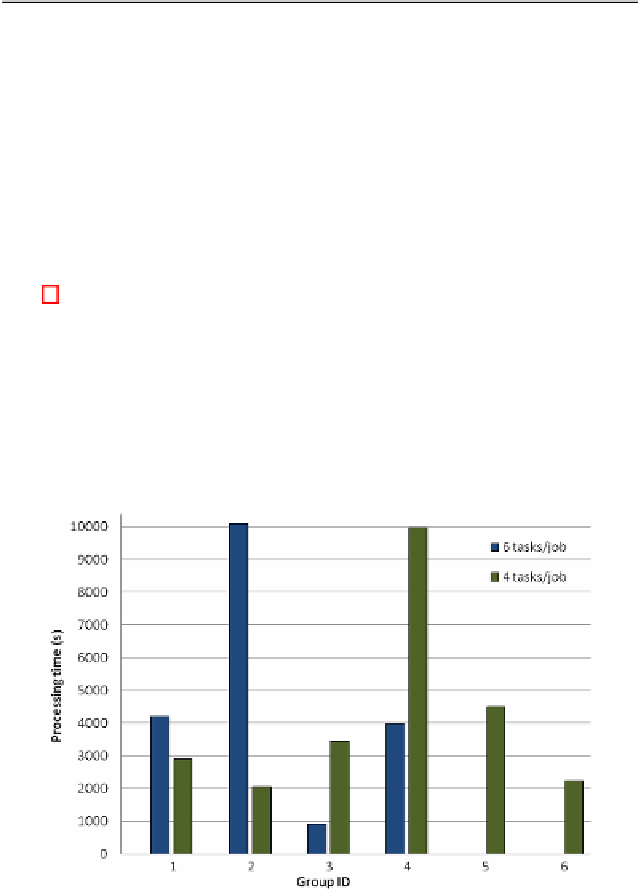
Table 3.
Parallel execution times
using 4 tasks/job
using 6 tasks/job
group ID instances time (s)
group ID
instances
time (s)
1
4,5,10,21
2891
1
3,7,10,12,17,22
4212
2
1,8,22,23
2045
2
4,8,13,14,20,23
10124
3
24,9,11,7
3450
3
1,5,6,9,11,15
914
4
2,20,15,13
9976
4
2,16,18,19,22,24
3977
5
6,12,14,17
4500
6
3,16,18,19
2240
Based on data generated by MCell, FERNet creates a single plain text con-
taining the amount of photons collected every time step. For each instance, a
different file is generated and approximately 300 KB of storage space is needed.
Once the task is finished, the output is transfered to the broker/client that sub-
mitted the corresponding job.
The output generated by MCell consists in the positions of each molecule every
time step. The size of this file depends on the amount of molecules configured in
the simulation, resulting in files between 8 and 15 GB. These files are discarded
once the task is finished.
Figure 6 shows the processing times for each group of tasks. Each group of
tasks corresponds to a job that is launched in the grid/cloud infrastructure.
A JDF file defining the job and the corresponding tasks is created for each
job. The total processing time for sequential execution of the 24 instances is
approximately 10
.
81 hours. The parallel execution time is approximately 2
.
78
hours. Figure 6 shows that both grouping methods require approximately the
same time to complete all the considered instances. As MCell is designed as a
Fig. 6.
Processing times for parallel execution