Agriculture Reference
In-Depth Information
Great Plains region. Because Stephens, Jagger,
and Jagalene also have high-temperature adult-
plant (HTAP) resistance, these cultivars have not
been severely infected. However, races with
Yr9
virulence caused severe epidemics from 2000 to
2005 on susceptible cultivars that lacked any
effective resistance.
Other epidemics of stripe rust caused by the
introduction of new races are well documented.
The best example includes the introduction of the
wheat stripe rust pathogen to eastern Australia in
the late 1970s (Wellings and McIntosh 1987;
Wellings 2007), western Australian in 2002
(Wellings et al., 2003), and South Africa in the
mid-1990s (Pretorius et al., 1997). These long-
distance introductions of the wheat stripe rust
pathogen from one continent to another were
thought to be caused by inadvertent human activ-
ities. Once present in a new continent, stripe rust
spreads quickly to neighboring countries. This
was seen in the spread of the barley stripe rust
pathogen from Colombia to other South Ameri-
can countries and to Mexico and the US from
1975 to 1991 (Chen et al., 1995). The races with
virulence to
Yr9
which have rendered many cul-
tivars with the 1RS.1BL wheat-rye translocation
highly susceptible to stripe rust were likely an
introduction from outside the US.
Since the group of races with
Yr9
virulence
appeared in the US in 2000, numerous new races
with additional virulence have subsequently been
found. In 2000, the most common races were
virulent to the differential lines 'Lemhi', 'Heines
VII', 'Lee', 'Fielder', 'Express', 'AVS/6*Yr8',
'AVS/6*Yr9', 'Clement', 'Compair', and
'Produra'. Since then a large number of races with
additional virulence to the differential cultivars
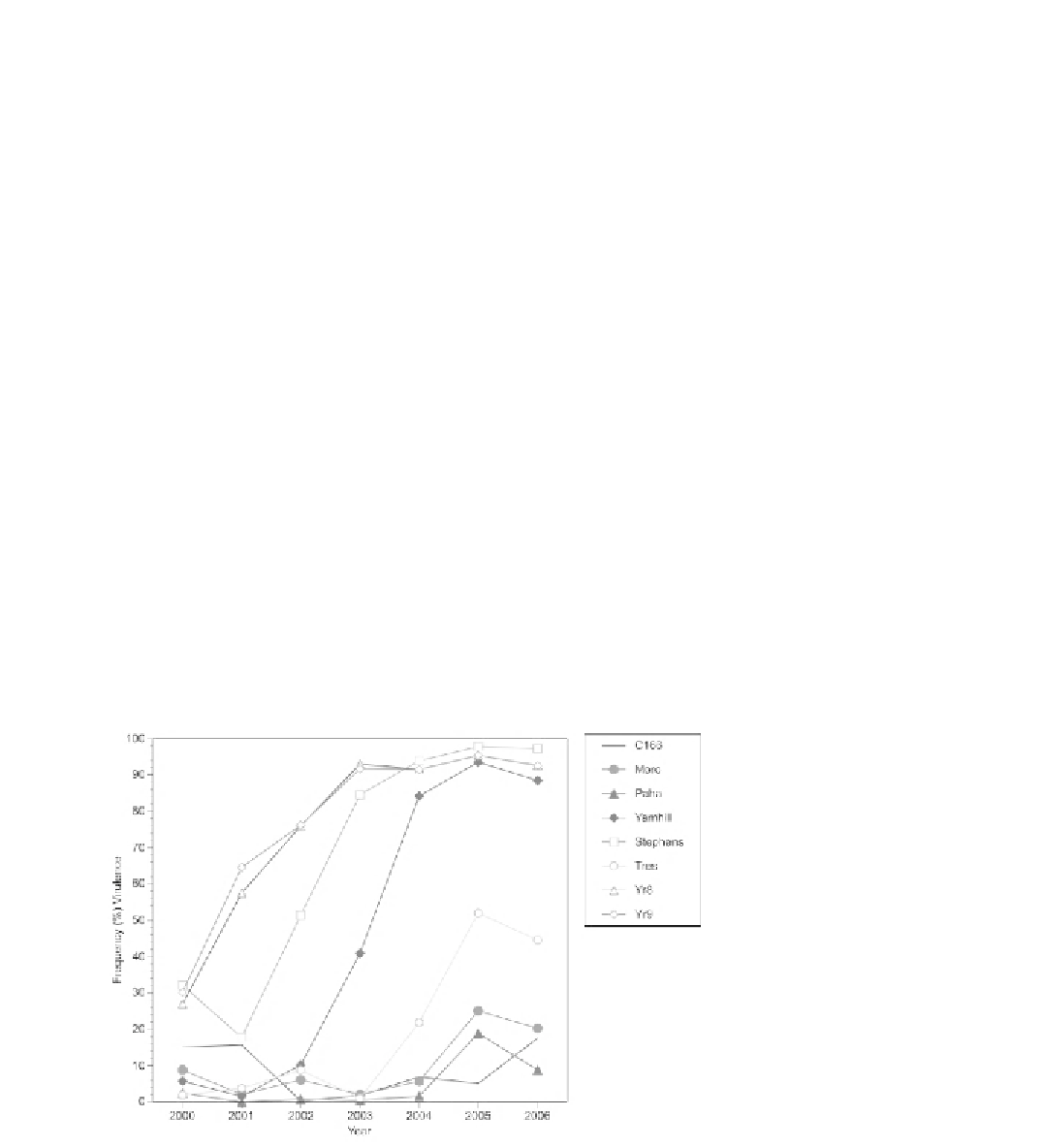
Tres, Stephens, Yamhill, and Chinese 166 have
been detected (Fig.5.2). Races with virulence to
Stephens, Yamhill,
Yr8
, and
Yr9
have been the
most common races in the US since 2003. In the
Pacifi c Northwest, races with virulence to the cul-
tivars Moro (
Yr10
and
YrMor
) and Paha were
detected in 2005. These new races have caused
several previously resistant cultivars to become
susceptible, or they have reduced the resistance
level in cultivars with race-specifi c resistance and
non-race-specifi c HTAP resistance (Chen 2005,
2007).
Molecular variation
Chen et al. (1993) used RAPD markers to examine
molecular variation in
P. striiformis
f. sp.
tritici
.
DNA polymorphism was detected among races
and among single-spore isolates within races.
Fig. 5.2
Frequency (%) of
isolates of
Puccinia striiformis
f. sp.
tritici
with virulences to
selected wheat genotypes in
the US from 2000 to 2006.
'Chinese 166' (C166) has
resistance gene
Yr1
; 'Moro',
Yr10
and
YrMor
; 'Paha',
YrPa1
,
YrPa2
, and
YrPa3
;
'Yamhill',
Yr2
,
Yr4a
, and
YrYam
; 'Stephens',
Yr3a
,
YrS
,
and
YrSte
; and 'Tres',
YrTr1
,
and
YrTr2
. The
Yr8
and
Yr9
near-isogenic lines are in
the Avocet-susceptible (AVS)
background.