Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
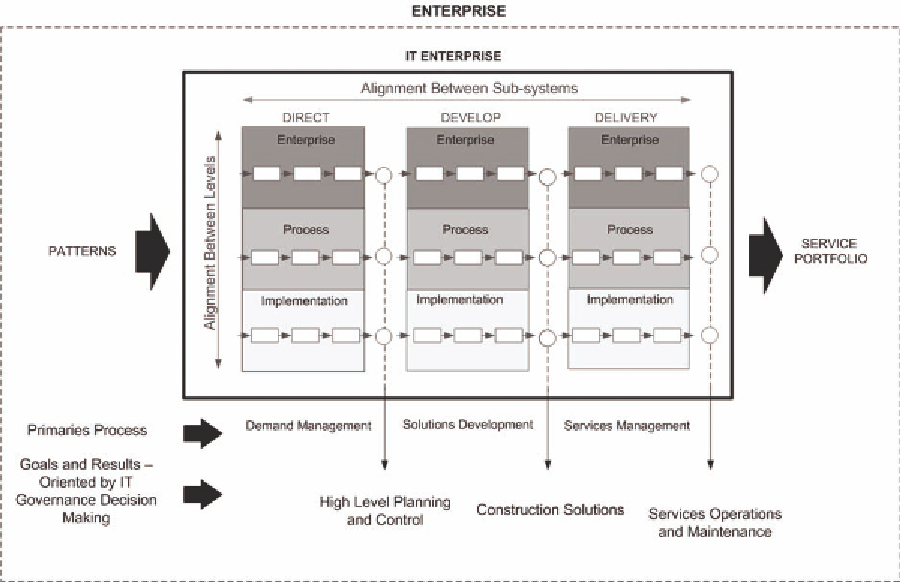
Figure 1. Model of systems and subsystems that comprise an IT Enterprise
ganization resources. . Service requests can be met
by the capacity of existing operational services.
For example, provisioning an e-mail account for
a user is a service request and the establishment
of a new e-mail service is a project request. An
incident report is a service where incidents or
problems in existing operational services are re-
ported and quality service is expected within the
time agreed upon with its consumers.
Regardless of what the subsystem is, IT Gov-
ernance monitors compliance with decisions by
means of performance indicators and control
objectives.
For Direct, the selected performance indicators
refer to IT financial management. These indicators
are obtained in COBIT, from a process called IT
investment management. The goal of control can
be defined as a desired outcome statement or the
purpose to be achieved on the implementation
level of an IT unit. A control objective is chosen in
order to mitigate risks to prevent compliance with
the decisions taken. Risk mitigation is a procedure
that can be used to support the identification of
control objectives. So as to customize control ob-
jectives accordingly with the Direct governance's
decisions, you can investigate and identify the
causes of risks that generate the degradation of
performance indicators or adopt and adapt control
objectives or available controls in the collection
of best practices from COBIT.
Control objectives chosen and adapted from
COBIT for IT financial management are financial
control, control of prioritizing investments, bud-
get control, cost and benefit control. The process
level includes activities that enable Macro-process
Demand Management modeling, which is divided
into two processes: Fulfilling Demand Requests
and Customer Relationships (Betz, 2007).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search