Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
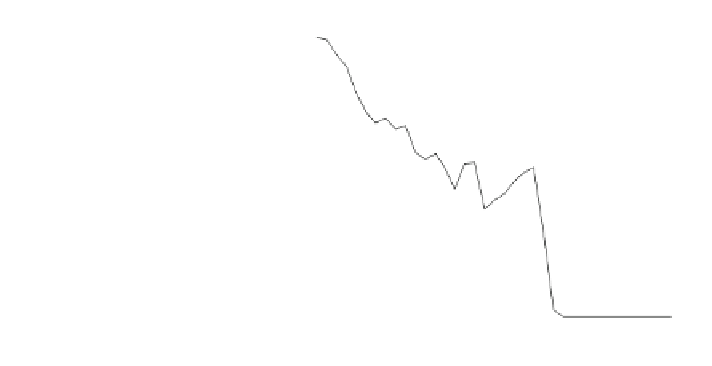
Fig. 9.23
Number of
differences among parents for
a run of the GA with 300
parents, 150 children, and
SVC
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
0
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
Number of iterations
Table 9.5
Comparison between CCR obtained in the preliminary study (1st row) and CCR
obtained with the genetic algorithm (2nd row)
Evaluation methods
Number of electrodes
in the predictive model
CCR
Mean
Standard deviation
CART
58
33.98
5.15
CART
1
86.68
1.87
9.7
Conclusions
This chapter presents a system for the automatic detection of human mental states of
alertness using EEG data and wavelet decomposition. This contribution is also
coupled with a complete protocol of data acquisition, a data validation procedure
and a feature selection strategy. Initially, we proposed a criterion to obtain a
summarized data matrix in two dimensions. Given the disappointing results
obtained by classifying all of the available data, a GA was used as a feature
selection step to re
ne it. This allowed obtaining a reliable classi
cation model that
achieves average of classi
cation accuracy equal to 86.68 % with a standard
deviation of 1.87 %. The algorithm also selects only a single electrode from the 58
that were initially available; this greatly enhances the possibility of applying the
proposed system in real-world scenarios.
An exchange with neurobiologists now seems necessary to link the results
obtained by the GA to human physiology. A new campaign to collect EEG data and
increase the number of participants included in the study has been undertaken.
Increasing the number of data should allow us to improve the precision of the estimate
of CCR and thus reduce the number of solutions that have the same score at the end of