Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
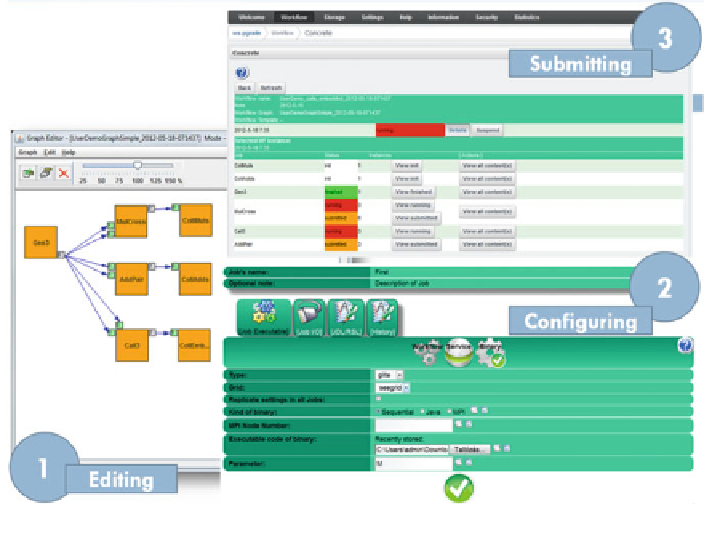
Fig. 2.2
The three generic workflow development phases in WS-PGRADE
2.5.2.1 The Editing Phase: Creation of the Work
ow Graph
The users construct their abstract work
ows in this phase. Practically, it covers the
work
ow graphical designer and
visualizer tool, the Graph Editor of WS-PGRADE (Fig.
2.3
). The structure of WS-
PGRADE work
ow graph creation by the interactive, online work
ows are represented by directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) as shown
in Fig.
2.3
. The DAG-based structure is the static skeleton of a work
ow in WS-
PGRADE. The nodes of the graph are abstract represenations of jobs (or service
calls). Each job must have a name, and job names are unique within a given
work
ow through input
and output ports. An output port of a job connected to an input port of a different
job is called a channel. Channels are directed edges of a graph, directed from the
output ports toward the input ports. A single port must be either an input or an
output port of a given job.
A job in a work
ow. The job communicates with other jobs of the work
ow may have single and parametric input ports (which should
be speci
ed in the next, the con
guring phase of work
ow development when
concrete work
ow). If a node has only single
input ports, it is executed only once as a single instance processing the single inputs
of every input ports. These nodes are called normal nodes. If a node has at least one
parametric input port it is called parametric node. If a parametric node has one
parametric input port, it will be executed in as many instances as the nukmber of
ow is de
ned from abstract work
files that arrive on the parametric input port (Manual 2014).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search