Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
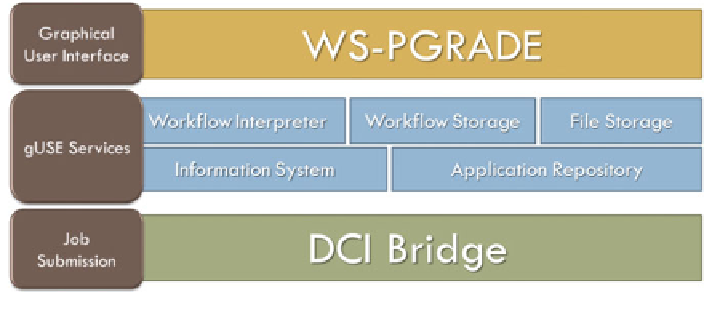
Fig. 2.1
The three-tier architecture of WS-PGRADE/gUSE
2.4 Architectural Overview
The main goal of designing the multitier architecture of WS-PGRADE/gUSE was
to enable versatile access to many different kinds of DCIs and data storage by
different kinds of user interfaces. This access can be technically performed through
the DCI Bridge job submission service which is in the bottom within the gUSE
architectural layers as shown in Fig.
2.1
, and via the Data Avenue Blacktop service
DCI Bridge
5
is a web service-based application providing standard access to
various DCIs. It connects through its DCI plug-ins to the external DCI resources.
When a user submits a work
ow, its job components are submitted transparently
into the various DCI systems via the DCI Bridge service using its standard OGSA
Basic Execution Service 1.0 (BES) interface. As a result, the access protocol and all
the technical details of the various DCI systems are totally hidden behind the BES
interface. The job description language of BES is the standardized Job Submission
The DCIs supported by DCI Bridge are the followings:
Clusters (PBS, LSF, MOAB, SGE)
Grids (ARC, gLite, GT2, GT4, GT5, UNICORE)
Supercomputers (e.g., via UNICORE)
Desktop grids (BOINC)
Clouds (via CloudBroker Platform, GAE, as well as EC2-based Cloud Access).
The middle tier of the gUSE architecture contains the high-level gUSE services.
The Work
ow Storage stores every piece of information that is needed to de
ne a
work
ow (graph structure description, input
files pointers, output
files pointers,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search