Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
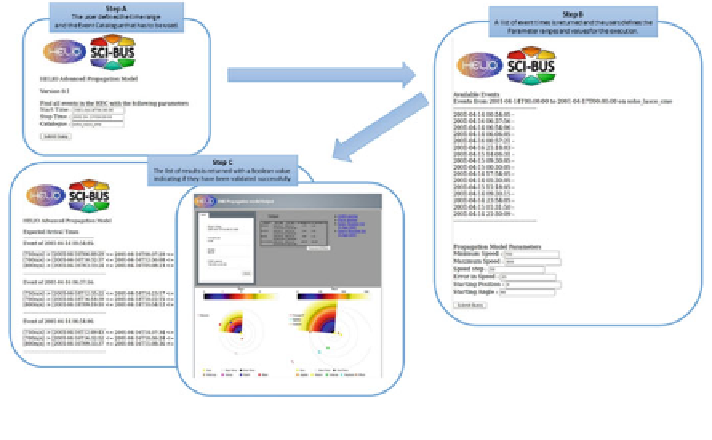
Fig. 14.2 The advanced propagation model portlet of HELIOGate
events at the target. In this last step, the user selects the results the parameter which
had a successful validation and analyzes the propagation simulation.
The advanced propagation model is implemented as a portlet on top of the gUSE
ASM API for the submission, execution, and con
guration of workflows. The
portlet implements a model that is similar to the assisted validated parametric model
at the bottom of Fig.
14.1
with two relevant differences. First, it executes an assisted
validated parametric model for each event within a time range, so it is a statistical
extension of this model. Second, it constraints how the parameters of the model are
inferred from the event catalogues, letting the user modify a range for the speed,
de
ne values for the remaining parameters, and use the lift of time of the coronal
mass ejections directly from the catalogues. The portlet also constraints the vali-
dation of the results by checking a speci
c catalogue for events at Earth and
returning true if a signature event of the coronal mass ejection was found within the
expected time of arrival predicted by the model.
These constraints have permitted an optimization of the portlet that used the
workflow only for the computationally intensive part (the parameter sweep execu-
tion of the propagation model), while the query of the event catalogues is executed
directly in the code of the portlet to avoid any overhead in the execution time.
14.5 Data Processing
HELIOGate is also used as a data processing tool as its computational and storage
facilities are very useful for data- and computation-intensive applications of image
processing. Two examples of such data processing applications (illustrated in
Search WWH ::

Custom Search