Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
It is evident from the above equation that multi-frequency network func-
tions quantify the fundamental and harmonic components of the fre-
quency response of nonlinear time-varying systems.
2.3 Multi-Frequency Transfer Functions
It is well known that the transfer function of linear time-invariant
systems completely characterizes the behavior of the systems in the fre-
quency domain. It is perhaps less well known that Zadeh's bi-frequency
transfer function
defined as
where and are the output and input frequencies, respectively, depicts
the behavior of linear time-varying systems in the frequency
domain
effectively. The output is obtained from
The corresponding time-varying network function is obtained from the
inverse transform
If i.e. is a single-tone at with unit amplitude.
Because we have This result
reveals that represents the aliasing transfer function of the
system from the input at the frequency
to the output at the
frequency
To analyze nonlinear time-varying systems in the frequency domain,
we extend the definition of Zadeh's bi-frequency for linear time-varying
systems to nonlinear time-varying systems by introducing the following
multi-frequency transfer function

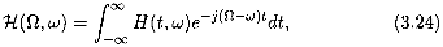
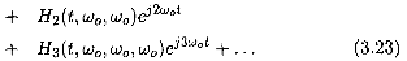
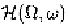

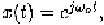
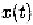
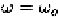
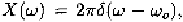
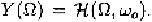
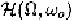
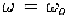
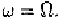
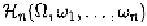
Search WWH ::

Custom Search