Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
are usually biased in strong inversion where is the
surface potential and is the Fermi potential [40]. The power of
the flicker noise originated in the channel is given by [98]
where is the drain-source quiescent current.
W
and
L
are the
width and length of the channel, respectively, is the gate transcon-
ductance, is the gate capacitance per unit area, and is the sur-
face mobility of charge carriers in the channel. MOSFET transistors
exhibit the highest noise among all active integrated devices [98].
As compared with BJTs, the corner frequency of the flicker noise of
MOSFET transistors could extend to mega Hertz ranges [2].
The thermal noise generated by a MOSFET transistor in saturation
is mainly due to the fluctuation in the drift current in the channel
[40]. The fluctuation in the diffusion current is negligible as the drift
current predominates over the diffusion current when the device is in
the strong inversion. The thermal noise of the drift current is given
by
[101]
where and are the gate transconductance and substrate transcon-
ductance, respectively.
Eq.(l 1.104) is valid only in the saturation region. It gives erroneous
results if the device is in the triode region because in this region
and zero thermal noise is predicted. In [102], the
channel conductance, is added to (11.104) to represent the thermal
noise generated by the device in ohmic region.
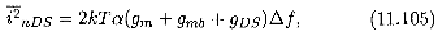
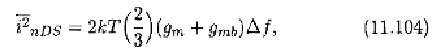

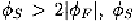


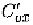


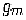
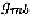

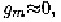

Search WWH ::

Custom Search