Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where
is a pulse shape function and
is the time at which the
pulse occurs. Note
is causal. The distribution of
is Poisson.
The power spectral density of
is given by Curson's theorem
[92,
93]
where is the Fourier transform of The band width of shot
noise is inversely proportional to the transit time required by the
carriers to cross the depletion regions, and is in high gigahertz ranges
[89]. Shot noise is often treated as a stationary white process. In the
extreme case where is approximated by Dirac impulse function
because we have the following Schottky's theorem
for the power spectral density of the shot noise of pn-junctions [56]
where is the average forward biasing current of the pn-junction
and is the charge of an electron. It should be noted
that the above result is only valid for where is the
time for mobile carriers to cross the potential barriers.
Flicker noise
: Flicker noise, also known as noise, exists in both
active devices and passive resistors. The mechanism of noise
in semiconductor devices has been studied extensively and tends to
converge to two basic
noise theories :
Carrier mobility fluctuation model of flicker noise
[94] - Flicker
noise is generated by the scattering of mobile carriers due to the
collision with the crystal lattice of silicon and impurities.
Carrier density fluctuation model of flicker noise
[95] - Flicker
noise is caused by the trapping and de-trapping of the mobile
carriers in the traps located at the surface of gate oxide.




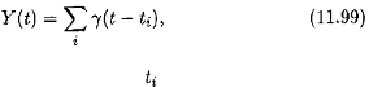
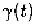
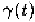

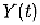
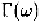

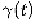
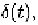



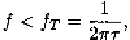
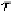
Search WWH ::

Custom Search