Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
and
I
denotes an identity matrix of appropriate dimensions. Note that
because (11.9) holds for
M
is frequency
dependent.
P
, on the other hand, is only related to the input frequency.
Once is available, can be obtained from (11.2) and the
complete response is obtained from
Let us now examine the properties of the preceding frequency analysis
algorithm in detail :
The infinite summation of Dirac impulse function terms in (11.9)
reveals that the frequency response of periodically switched linear
circuits to a single-tone input at frequency
contains an infinite
number of frequency components at frequencies
The frequency component at frequency
is called the
baseband component and that at frequency
is called the
sideband component.
The method is exact. No approximation is made in the derivation
of the method. To obtain the accurate frequency response numeri-
cally, both and must be computed to high precision. They
can be computed using the multi-step numerical Laplace inversion
algorithms given in Chapter 4.
Compared with the analysis of ideal switched capacitor networks, the
following additional computation is required in the frequency analysis
of periodically switched liner circuits
Computation of
and
Computation of
LU-decomposition of
and subsequent forward and
backward substitutions in solving
Frequency analysis of periodically switched linear circuits is thereby
more costly.



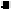


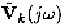

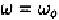
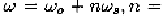
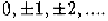
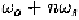

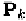
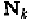
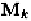
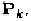
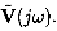


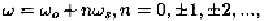
Search WWH ::

Custom Search