Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1. Frequency Response
The frequency response of ideal linear switched capacitor networks is
obtained from of algebraic equations obtained from charge
conservation at switching instants [34]. Because switched capacitor net-
works are a subset of general periodically switched circuits, they can
be handled by methods for general periodically switched circuits. For
this reason, frequency analysis of ideal switched capacitor networks will
not be presented here. Interested readers are referred to references at
the end of the topic, such as [5], for the details on the analysis of ideal
switched capacitor networks. Unlike ideal switched capacitor networks,
the incomplete charge transfer characteristics of periodically switched
linear circuits, due to the inclusion of resistors, inductors, and non-ideal
operational amplifiers in the configuration of these circuits, requires that
the circuits be depicted by differential equations. The state of the net-
work variables at the end of each clock phase be determined by solving
these differential equations using numerical integration.
It was shown in Chapter 2 that the behavior of a periodically switched
linear circuit in the time domain with input
and a total of
K
clock phases can be depicted by
for The two Dirac delta functions represent the injection
of the initial conditions of elements with memory at the beginning of the
clock phase accounting for the effect of the initial charge
of capacitors and the initial flux of inductors, and the extraction of the
final conditions of these elements at so that vanishes
outside the clock phase Eq.(11.1) is thus valid for The
frequency domain response of the circuit is obtained by applying Fourier
transform
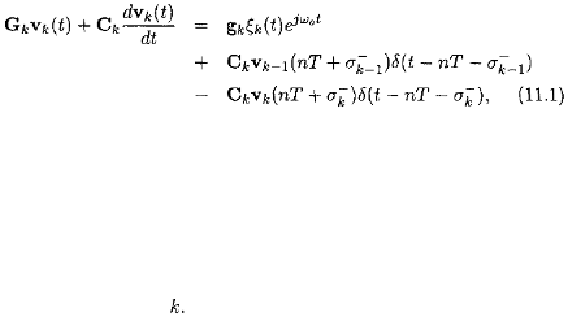

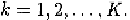
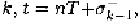

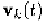
Search WWH ::

Custom Search