Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
is no switching condition violation. It is only after no switching condi-
tion violations exist, the final topology of the circuit at the switching
instant can be established, and the two-step algorithms introduced
in Chapter 5 can be employed to compute
from
Once
is available, simulation proceeds forward in time.
It should be emphasized that at the switching instant of each
internally controlled switch, not only the detection of whether impulsive
network variables may be generated at the switching instant must be
conducted, the value of the network variables at the time instant imme-
diately after the switching, i.e must also be carried out to update
the initial condition of the circuit so that the detection of the switching
of other internally controlled switches at the same time instant can be
carried out.
4. Examples
In this section we use the linear voltage regulator shown in Fig.8.5
as an example to demonstrate the analysis of circuits with internally
controlled switches.
The basic operation of the voltage regulator is as follows : The MOS-
FET switch is controlled by an external clock with variable duty cycle.
When the supply voltage
E
supplies a current to the series induc-
tor
L
and the load resistor
R.
Because the output is current, the value
of the load resistor
R
is small. The functionality of the shunt capacitor
C
is to sustain the output voltage, whereas that of the series inductor
L
is to sustain the output current in the absence of
E.
The value of
L
and that of
C
must, therefore, be sufficiently large so that the ripple of
the output current and that of the output voltage during the absence of
E
are small. When
E
is disconnected from the load. The output
current is sustained by the magnetic energy stored in the series inductor
and the electric energy stored in the shunt capacitor. By adjusting the
duty cycle of the switching MOSFET given by
the average
output current can be controlled and is given by



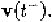





Search WWH ::

Custom Search