Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
where is the standard deviation of the clock jitter and
N
(0,1) is a
normal random number generator with zero mean and unity standard
deviation.
8.
Summary
Sampled-data simulation, an efficient, accurate, and absolutely stable
time domain algorithm for periodically switched linear circuits has been
developed in this chapter. We have shown that this algorithm computes
response, sensitivity, mean and variance of the response, output noise
power in the presence of white noise sources, and the effect of clock
jitter of periodically switched linear circuits at time points of a fixed
time interval. In computation of the time domain response, only one
matrix multiplication and one vector addition are needed in each time
step. Once the transition matrix and zero-state response vector
are computed to high precision, the response can be obtained
with a very high degree of accuracy. The inconsistent initial condi-
tions arising from ideal switching are handled using numerical Laplace
inversion based two-step algorithm effectively. In sensitivity analysis,
the sensitivity of the response of periodically switched linear circuits
to a circuit parameter is computed at time points of a fixed interval.
No approximation is made. A drawback of this method in sensitivity
analysis is that it yields the sensitivity of the response to one circuit pa-
rameter, rather than to all circuit parameters, in one network analysis.
It is therefore computationally costly if sensitivities to a large number
of circuit parameters are needed. In statistical analysis, the first-order
second-moment method that yields the mean and variance of the re-
sponse of periodically switched linear circuits without multiple analyses
of the circuits has been introduced. As compared with Monte Carlo
based methods, the method is computationally efficient. Because only
up to the second-order moments were considered in the derivation of the
first-order second-moment method, the accuracy of the method deterio-
rates if the coefficient of variance of circuit parameters is large. In noise
analysis, white noise signals of a given circuit are represented by a train
of pulses with the pulse width set by the noise bandwidth of the circuit
and the pulse amplitude set by the output noise power of the circuits
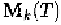


Search WWH ::

Custom Search