Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Chapter 5
INCONSISTENT INITIAL CONDITIONS
Inconsistent initial conditions arise from ideal switching and cause the
value of network variables immediately before switching to differ from
that immediately after switching. Because the topology of switching
circuits may change at switching instants, the value of network variables
immediately before switching, denoted by can not be used to
compute the response of circuits after switching. Instead, the value of the
network variables immediately after switching, denoted by
must
be used to continue integration.
This chapter investigates computer
methods that compute
from
Section 1 investigates the cause of the inconsistent initial conditions
of mixed-mode switching circuits. Section 2 examines the two-step al-
gorithm derived from numerical Laplace inversion and its applications.
We show that the two-step algorithm is an accurate and computationally
efficient algorithm that yields from of linear circuits. Sec-
tion 3 shows that the conventional backward Euler formula is capable
of yielding from This approach is applicable to mixed-
mode switching circuits with both linear and nonlinear elements. In
addition, it is capable of computing the area of impulses at switching
instants. Section 4 presents a Taylor series based approach for deriving
from In Section 5, we show that the inconsistent initial
conditions encountered in nonlinear circuits can also be handled using
Volterra functional series based methods.
Section 6 is concerned with
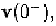
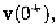
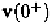


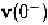

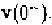


Search WWH ::

Custom Search