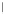Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Homo
21
Pongidae
22
Catarrhini
?
?
Symphalangus
HSA15
Hylobates
15
HSA21
25
2
Nomascus
Macaca
HSA7
HSA20
Cercopithecus
9
HSA22
Simii
Colobus
13
Platyrrhini
Callithrix
15
Primates
Cebus
9
?
Pithecia
Microcebus
Cheirogaleus
Eulemur
9
1
Prosimii
HSA9
Ancestral
eutherian
HSA21
1
Scandentia
HSA3
Tupaia
7
Paradoxurus
11
Carnivora
Felis
C2
Bos
1
Artiodactyla
Sus
13
Lagomorpha
Oryctolagus
14
HSA22 and 16
Rodentia
Mus
16
Figure 2.7.
Evolution of the equivalent of human chromosome 21 (HSA21) in eutherian
mammals (after Richard and Dutrillaux, 1998). HSA21 (open rectangle) formed a large
and unique chromosome with HSA3 (dark rectangle) in the eutherian ancestor. This
chromosome was conserved without significant alterations only in
Microcebus murinus
(lesser mouse lemur) and
Cheirogaleus major
(greater dwarf lemur),
Paradoxurus
hermaphroditus
(common palm civet) and
Sus scrofa
(pig). It underwent inversions (open
circles) in
Tupaia glis
(tree shrew) and
Bos taurus
(cow) or various translocations involving
the portion corresponding to HSA3 (dark squares) in
Eulemur fulvus
(brown lemur),
Felis
catus
(cat),
Oryctolagus cuniculus
(rabbit), and
Mus musculus
(mouse). In the primates, two
independent fissions (arrowed) occurred. In the Platyrrhini (New World monkeys), a
small segment of HSA3 remained attached to HSA21 and this chromosome then
underwent further rearrangements: an inversion in
Callithrix jacchus
(marmoset), the
addition of heterochromatin in
Cebus capuchinus
(capuchin monkey) and translocation in
Pithecia pithecia
(saki). HSA21 was formed in the common ancestor of all Catarrhini (Old
World monkeys) and underwent translocations (open squares) with various equivalents of
human chromosomes (grey rectangles) in all Cercopithecidae viz.
Macaca sylvana
(Barbary ape),
Cercopithecus mona
(Mona monkey),
Colobus abyssinicus
(northern black and
white colobus),
Symphalangus syndactylus
(simiang) and
Hylobates lar
(white-handed
gibbon). HSA21 was conserved without visible alteration in
Nomascus concolor
(black
gibbon) and in the great apes (
Gorilla gorilla
,
Pan troglodytes
and
Pongo pygmeus
). The
number of the carrier chromosome of each species is indicated.