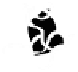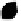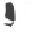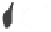Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
extant thrombin. P4 also contained residues analogous to Asn36, Gln37, Glu38
(chymotrypsin numbering) of the vitamin K-dependent factor ancestral protein
(Glu38 belongs to the S3
site of extant thrombin). In early mammalian protein C,
these three residues had become lysines which would have served to increase the
net positive charge in this area. Since this region binds thrombomodulin in
extant protein C (Wacey
et al
., 1993; Greengard
et al
., 1994; Vinceno
et al
., 1995;
Grinnell
et al
., 1994), the P4 site may represent the nascent thrombomodulin-
binding patch in early mammalian protein C.
Figure 10.5
depicts the envisaged
evolutionary transformation of the primitive original fibrinogen/ thrombomod-
ulin-binding patch into a region specialised for thrombomodulin binding. In
extant protein C, substitution of Trp76 by Arg has served to increase further the
anionic potential, and thus specificity, of this patch. Finally, it should be noted
that the anionic residues of P4 (K36, K37, K38, R74, K148, R149, R151) in early
mammalian protein C appear to have undergone relatively few subsequent substi-
tutions in order to 'fine-tune' binding to thrombomodulin. Thus the P4 patch in
early mammalian protein C was probably of the minimum size required to bind
thrombomodulin, and was subsequently extended and refined by evolution.
The binding patch P3 (comprising anionic residues Lys20, Arg23, Lys159, and
Arg188) of the vitamin K-dependent factor ancestral protein is also apparent in
early mammalian protein C. However, in the latter molecule, this patch was less
expansive and confined to a higher latitude in the molecule. The apparent migra-
tion of the patch away from the equatorial belt appears to have continued during
P3
P3
P3
P4
P4
Figure 10.5.
The electrostatic profiles of the vitamin K-dependent factor ancestral
protein (top, alpha carbon backbone is shown as a ribbon, electrostatic surface is solid),
early mammalian protein C (bottom right, alpha carbon backbone is shown as a ribbon,
electrostatic surface is solid) and extant human protein C (bottom left, alpha carbon
backbone is shown as a ribbon, electrostatic surface is solid) are shown (Wacey
et al
.,
1997). The electrostatic equipotential surfaces are contoured at +1 kcalmol
-1
. The view is
towards the active site canyon. The locations of the anionic patches P3 and P4 are
indicated.