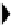Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
1. Duplication
A
P
A
P
A'
P
2. Unequal homologous
Alu-Alu
recombination
A
P
A'
P
A
P
A'
P
A
P
B / E
3. Duplication
A
P
B / E
A
P
B
E
Figure 9.7.
Three-step scenario in the evolution of the glycophorin gene family.
A:
GYPA,
B:
GYPB,
E:
GYPE.
In the second step, unequal
Alu
-
Alu
recombination
created the subsequently duplicated B/E gene locus. Vertical triangles denote
Alu
repeats,
open boxes the genes A, A
, B/E, B, and E, whereas a filled box - 'precursor' sequence (P)
that became an integral part of the contemporary genes B and E (redrawn from Labuda
et
al
., 1995).
High resolution genetic mapping studies have provided evidence for both
'hotspots' and 'coldspots' of recombination (Nagaraja
et al
., 1997; Shiroishi
et al
.,
1993). A frequent disease-associated recombinational hotspot in the human
genome occurs at 17p11.2-p12 where a CMT1A-REP tandem repeat mediates
meiotic crossing over events through chromosome misalignment. Humans and
chimpanzees have two copies of this repeat whilst gorilla, orangutan and gibbon
have only a single copy (Kiyosawa and Chance, 1996). The CMT1A-REP repeat
must therefore have appeared before the divergence of chimpanzee and human.
The repeat contains a
mariner
-like element in the vicinity of the recombination
hotspot and, since this element occurs in association with the CMT1A-REP
repeat in all primates, it must have predated the emergence of the proximal and
distal copies of the repeat in the human-chimpanzee common ancestor (Kiyosawa
and Chance, 1996). Interestingly, the
mariner
element of
Drosophila
exhibits
sequence homologies to transposons from
Caenorhabditis elegans
as well as hep-
tamer and nonamer signal sequences of the vertebrate immunoglobulin somatic
recombination pathway (Dreyfus 1992). Whether these homologies that tran-
scend the invertebrate-vertebrate divide are merely coincidental, or whether they