Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
51 functional
V
H
segments
~30
D segments
6
J
H
segments
C
H
genes
µδ
3
1
2
1
2
4
1
2
1234
51
~2500 kb
~45 kb
6.5 kb
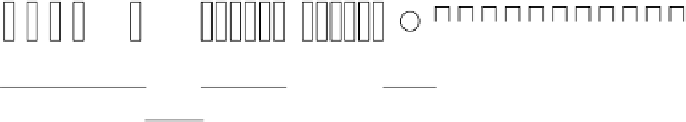
Figure 4.29.
Schematic organization of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain (
IGHV
)
locus.
light chain locus contains 76 V
κ
genes (
IGKV
) and pseudogenes, 5
functional J
κ
segments (
IGKJ
) and a single C
κ
gene (
IGKC
). This locus consists of
two copies of a DNA region arranged with opposite polarity (Weichhold
et al
.,
1993), the result of an intra-locus duplication which has occurred since the diver-
gence of human and chimpanzee (Ermert
et al
., 1995). The
The
light chain locus con-
tains contains 36 functional V
λ
genes (
IGLV
), 33 V
λ
pseudogenes, 34 V
λ
'relics'
containing large deletions or insertions, 6 J
λ
segments (
IGLJ
) and 6 C
λ
genes
(
IGLC
) (Kawasaki
et al
., 1997). In addition to the above, 8 V
H
segments (
IGHV2
)
and a cluster of D segments (
IGHDY2
) have been identified on chromosome
15q11.2 with a further 16 V
H
segments (
IGHV3
) on chromosome 16p11.2
(Tomlinson
et al
., 1994). These 'orphon' V
H
sequences are thought to have been
translocated to chromosomes 15 and 16 some 20 Myrs ago (Matsuda and Honjo,
1996) and ~40% may be functional. A small cluster of orphon V
sequences has
also been found on chromosome 22, and flanking direct and inverted repeats have
been invoked to account for their transposition (Borden
et al
., 1990).
It has been apparent for some time that the heavy and light immunoglobulin
chains are homologous and that these proteins must have been assembled by
extensive duplication of a short ancestral 100 amino acid polypeptide chain (Hill
et al
., 1966). This domain, the immunoglobulin fold, has now been found in a very
wide array of different proteins throughout the animal kingdom. The
immunoglobulins of the immune system appear however to be a vertebrate cre-
ation (Schluter
et al
., 1997).
The immunoglobulin genes are thought to have originated very early in the
evolution of the jawed vertebrates (Rast
et al.
, 1997). Phylogenetic analyses of the
human V
H
heavy chain genes (Haino
et al.
, 1994; Vargas-Madrazo
et al.
, 1997), C
H
genes (Takahashi
et al.
, 1982), V
λ
light chain genes and pseudogenes (Kawasaki
et
al
., 1997) and V
light chain genes (Kurth
et al.
, 1993; Sitnikova and Nei 1998;
Sitnikova and Su 1998; Vargas-Madrazo
et al.
, 1997) are consistent with a history
of multiple, successive duplication events, both extensive and of more limited
extent, during the evolution of all branches of the immunoglobulin gene family.
This mode of evolution is reminiscent of a 'birth and death process' rather than
any mechanism of concerted evolution (Section 4.2.1). Some immunoglobulin
genes have have been present in vertebrate genomes for >400 Myrs, others are
more recent creations that have emerged during the mammalian radiation
(reviewed by Andersson and Matsunaga, 1995; Matsuda and Honjo, 1996;
Schluter
et al.
, 1997). The expansion of the immunoglobulin gene family was