Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
Class II
Class III
Class I
Complement
proteins
Cytokines
DP
DZ
DO
DX
DQ
DR
TNF
B
C
A
Centromere
1000 kb
Class I-like
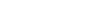
Figure 4.18.
Map of the human histocompatibility complex loci on 6p21.3.
In humans, the class I loci are
HLA-A
,
HLA-B,
and
HLA-C
(classical or type Ia)
and
HLA-E
,
HLA-F,
and
HLA-G
(non-classical or type Ib) (
Figure 4.18
). The class
I genes are interspersed with five MHC class I-related (MIC) loci (
MICA
,
MICB
,
MICC
,
MICD,
and
MICE
), five full-length pseudogenes (
HLA-H
,
HLA-J
,
HLA-
K
,
HLA-L,
and
HLA-X
) plus several truncated pseudogenes and remnants (
Figure
4.19
). The 5 MIC genes are distantly related to the hemochromatosis (
HFE
;
6p21.3) gene. The class II loci are clustered into three regions, HLA-DR (
HLA-
DRA
,
HLA-DRB1
,
HLA-DRB2
,
HLA-DRB3
,
HLA-DRB4,
and
HLA-DRB5;
NB.
HLA-DRB3
,
HLA-DRB4,
and
HLA-DRB5
may be variably present or
absent depending upon the haplotype), HLA-DQ (
HLA-DQA1
,
HLA-DQA2
,
HLA-DQB1
,
HLA-DQB2
,
HLA-DQB3
), and HLA-DP (
HLA-DPA1
,
HLA-
DPB1
,
HLA-DNA
) (
Figure 4.18
). The class I and II regions are separated by a
gene-dense 1100 kb region containing a number of so-called type III genes
including
BF
,
C2
,
C4A
,
C4B,
and
TNF
.
The ancestral MHC molecule appears to have been assembled by combining its
three constituent domains (peptide-binding domain, immunoglobulin-like
domain and membrane-anchoring domain) by exon shuffling (
Figure 4.20
).
Hughes and Nei (1993) estimated that the class II A and B genes diverged more
than 500 Myrs ago. Class I genes then emerged by duplication and divergence
during the primate radiation of the last 60 Myrs (Hughes and Yeager, 1997;
Kulski
et al
., 1997). The putative ancestral duplication(s) early in vertebrate evo-
lution (Chapter 2, section 2.1) may well have provided an impetus to the emer-
gence of the HLA complex in that the consequent redundancy could have created
opportunities for the emergence of a variety of accessory and effector molecules
(Kasahara
et al
., 1997). A scheme for the subsequent evolution of these genes is
presented in
Figure 4.21
.
100 kb
Figure 4.19.
Map of the class I region of the human histocompatibility complex (redrawn
from Wells and Parham, 1996).