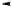Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
is also apparent when intron/exon distribution and codon usage for the active site
serine (Brenner, 1988) are considered: the alternative codons, TCN and AGY, can-
not be interconverted by a single nucleotide substitution. The genes encoding fac-
tors VII, IX, X, and protein C possess the AGY codon whilst the fibrinolytic
enzyme genes possess the TCN codon. Phylogenetic trees for the protease and
kringle domains are however not identical (Ikeo
et al
., 1995) suggesting that these
domains may have experienced different evolutionary histories. This implies that
in multidomain proteins such as the serine proteases, each domain can represent
an independent evolutionary unit.
3.6.4 Protein folds, primordial exons and the emergence of exon shuffling
Proteins are composed of combinations of secondary structural elements,
-helices
and
-sheets, which are connected by loop regions at the surface of the molecule.
Certain combinations of these elements (termed
motifs
or
folds
) are frequently used
+(C,P)
+M
+(B,D)
-(B,D)
+(A,E,L,N,R)
+H
+K
+B
+I
+F
+(G,S)
HP
C1s
PC
X
uPA
XII PL XI
TR
EL
AD,ME
C1r
PT
IX
VII
tPA
CFI
KL
CH
2
1
1
0
1
XI
2
1
1
0
1
uPA,tPA,XII
02
0
1
0
1
CH
02
2
1
0
0
1
EL
2
1
0
1
TR,KL
2
0
0
1
AD,ME
2
2
2
1
0
1
PT
0
1
1
VII,IX,X,PC
1
HP
AB
C
DE
FGHIK L
M
N
PR
S
Figure 3.9.
Evolution of the serine protease family (redrawn from Patthy, 1990). The
genealogy of the serine protease family was elucidated by reference to the known amino
acid sequences. Dashed lines indicate proteases whose gene structure has not yet been
established. 0, 1, 2 denote the phase class of the introns. Introns are labelled A to S, and
putative intron addition and removal events during evolution (consistent with the
genealogy based upon amino acid sequence data) are denoted by (+) and (
) respectively.
Protein abbreviations used are: HP, haptoglobin; Clr and Cls, complement factors Clr and
Cls; PT, prothrombin; PC, protein C; IX, X, VII, factors IX, X, VII; uPA, urokinase;
tPA, tissue-type plasminogen activator; XII, factor XII; PL, plasminogen and
apolipoprotein(a); XI, factor XI and pre-kallikrein; CFI, complement factor I; TR,
trypsin, KL, kallikreins; EL, elastases; CH, chymotrypsin; AD, ME, adipsin, medullasin,
mast cell proteases, cytotoxic lymphocyte proteases, cathepsin G.