Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
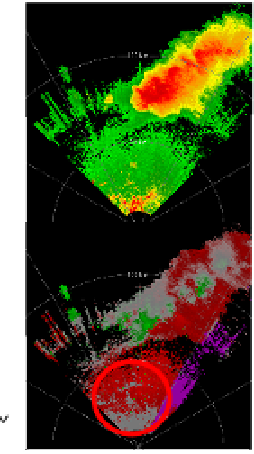
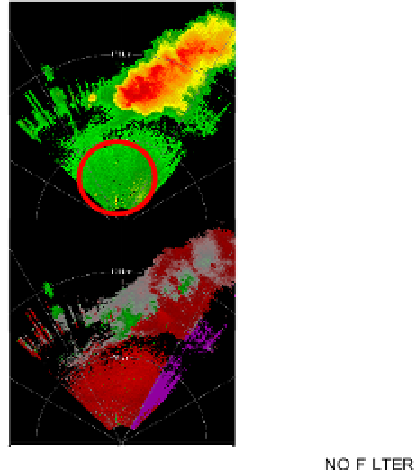
Fig. 14. Fields of reflectivities (top) and velocities (bottom) with no filter (right) and after
application of the CLEAN-AP. Close to the radar the strong reflectivities in the top right
panel encircled in red (red indicates > 50 dBZ) are caused by ground clutter which also
biases the velocities toward zero (lower right panel). CLEAN-AP eliminates most of the
clutter in both fields (left panels). To the NE within the yellow circle there are areas of near
zero velocities (lower panels gray areas are velocities within ±5 m s
-1
). These appear
unaffected by the filter. The data were collected with the agile beam phased array radar
(NWRT) in Norman, OK. (Figure adapted from Warde & Torres, 2009).
4.4 Hybrid spectrum width estimator
The spectrum width estimator (9) is deficient at narrow widths where significant bias
occurs. This shortcoming will be overcome with the Hybrid estimator which chooses an
appropriate equation depending on a rough initial estimate of
σ
v
(Meymaris et al., 2009).
Initial estimate of the spectrum width is made using thee estimators) (9),
ˆ
ˆ
RR
as in
(1) /
(2)
(Doviak & Zrnic, 2006 eq. 6.32) and an estimator based on
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
RR R
. Criteria
applied to the results produce three categories of widths, large, medium, and small. Then (9)
is used as estimate for the large category,
(1),
(2), and (3)
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
RR
for the medium and
(1) /
(2)
RR
for the
(1) /
(3)
small.
5. Observations of phenomena
Mesocylone refers to a rotational part of storm with the diameter of maximum wind
typically between 3 and 10 km. It is depicted with a couplet of Doppler velocity features (see
Fig. 9). Storms having mesocyclones can produce devastating tornadoes (Fig. 9 exhibits a
tornado vortex signature associated with the mesocylone), strong winds, and hail. Thus,
much effort has been devoted to detecting and quantifying these phenomena (No. 2 issue of
Weather and Forecasting, 1998). One of the motivating reasons for installing Doppler radars