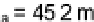Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
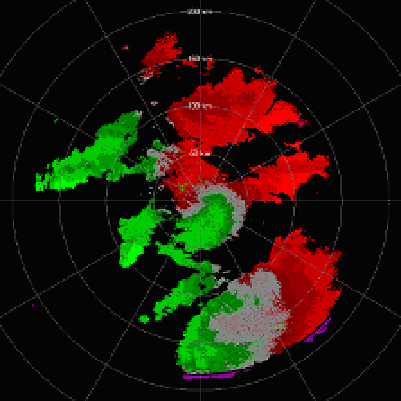
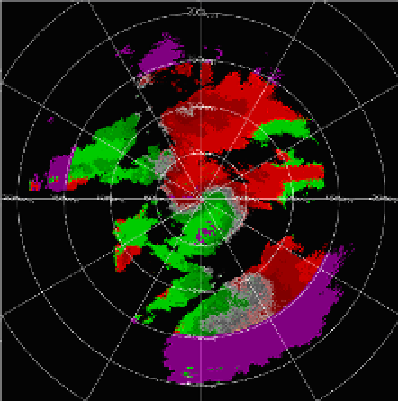
the research radar. Also, the large pink area of overlaid echoes has almost disappeared in
the measurement made utilizing the staggered PRT. The small circle closest to the radar
origin indicates overlaid echo contaminating the first trip velocities of the operational radar.
Fig. 11. Velocity fields of a storm system. Left: field obtained with the operational WSR-88D
radar in Oklahoma City on April 06, 2003, elevation 2.5 deg, batch mode with unambiguous
range of 148 km and velocity of 25.4 m s
-1
. Pink regions locate censored velocities which can
not be reliably recovered due to overlaid first and second trip echoes. Right: same as on the
left but obtained with the research WSR-88D (KOUN) utilizing staggered PRT. This radar is
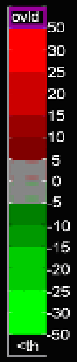
about 20 km south from the operational radar. The color bar indicates velocities (m s
-1
), red
away from and green toward the radar. (Figure adapted from Torres et al., 2003).
4.2 Oversampling techniques
Oversampling here indicates spacing of I, Q samples smaller than the pulse duration.
Operations on few of these range consecutive “oversamples” can reduce error in estimates
and/or data acquisition time (Torres & Zrnic, 2003). Simplest of operations is averaging in
range of oversampled spectral moments. Somewhat more involved is the whitening
transformation in which the signal vector
v =
[V(
m
,0), V(
m
,1),... V(
m
,
l
),....V(
m
,
L
)] consisting
of
L
oversampled correlated complex voltages is transformed into a set of
L
orthogonal
voltages (Torres & Zrnic, 2003). The time index
m
refers to the usual sample time and
l
to the
oversampled range time. The transformation takes the form
x
=
H
-1
v
with
H
related to the
normalized correlation matrix
C
of
v
via
C
=
H*H
T
. The correlation matrix can be pre-
computed (or measured e.g., Ivic et al., 2003) because it depends solely on the envelope of
the transmitted pulse and the baseband equivalent receiver filter shape for a uniform Z. The
L
transformed samples are independent and averaging of spectral moments obtained from
each (in absence of noise) yields smaller error of estimates. Whitening is effective at large
SNRs but fails otherwise. To achieve
L
independent samples the receiver filter bandwidth
needs to be increased
L
times over the matched filter bandwidth and this enhances the noise
by the same factor. In addition the whitening transformation also increases the noise hence