Geoscience Reference
In-Depth Information
The accuracy of the multiple Doppler radar analysis is evaluated using root-mean-square
errors in retrieved radial velocity (RMSE_VR) and vertical velocity (RMSE_W), defined as
follows:
1
ijkm
,,,
2
(4)
RMSE _ VR k
(
Vr
Vr
_
obs
)
N
ijm
,,
1
ijk
,,
true
2
(5)
RMSE _ W k
(
WW
)
N
2
ij
,
Average values of RMSE_VR and RMSE_W are computed at each vertical level after L-
BFGS optimization.
W
true
is the vertical velocity output by the CReSS model.
N
and
N
2 are
the number of individual samples used to compute the averages at a given layer.
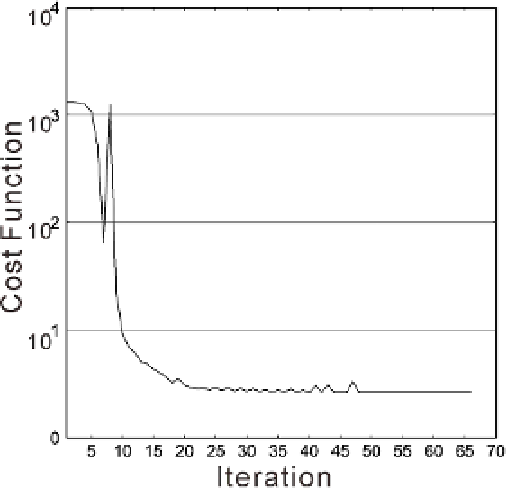
The L-BFGS optimization scheme is able to successfully minimize the cost function. Figure 6
shows the relationship between the value of the cost function and the number of iterations
performed. The value of the cost function is effectively constant after 20 iterations.
Fig. 6. Value of the cost function according to the number of iterations.
The results of the variational multiple Doppler radar analysis using volume scans with 30 PPIs
(experiment name: EL30) is shown in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8. Figure 7 shows that the EL30
experimental setup successfully retrieves the strong updraft core shown in the original model
output (Fig. 4). The EL30 results indicate a maximum updraft speed at 2 km ASL of 12 m s
-1
,
and successfully reproduce the anticlockwise rotation at this level. The downdraft region
located in the area of heavy precipitation to the east of the strong updraft is retrieved by EL30,
although the size of this downdraft region is too small (Fig. 4). The horizontal wind field
retrieved by EL30 is similar to the original model output (Fig. 4), but there are two major
discrepancies in vertical velocity. First, the strength of the updraft speed at 2 km ASL is
underestimated by 3 m s
-1
. Second, a spurious downdraft is identified to the southwest of the