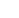Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
Use of current
imaging
modalities
Imaging
technique
Optical
MRI
PET
SPECT
X-ray CT
Ultrasound
Molecular
Type of
electromagnetic
radiation energy used
in image generation
Spatial resolution
Visible to near infrared
Radiowaves
High energy
γ
rays
Lower energy
γ
rays
X-rays
High frequency sounds
15-1000 nm
4-100 um
~1 mm-fMRI
1-2 mm
1-2 mm
12-50 um
50-200 um
50-500 um
Depth
< 1 cm
No limit
No limit
No limit
No limit
mm to cm
Scan time
Seconds
Minutes
Minutes
Seconds
Metabolism
Minutes to hours
seconds to minutes-
fMRI
Type of molecular
probe and quantity
of probes used
Activatable, direct or
indirect
micrograms to
milligrams
Activatable, direct or
indirect
micrograms to
milligrams
Radiolabeled, director
indirect
nanograms
Radiolabeled,
direct or indirect
nanograms
Limited activatable,
direct
micrograms to
milligrams
Imaging agents-
Contrast agents and
molecular probes
(Most of the imaging
agents can be found
from the Molecular
Imaging and contrast
Agent Database
(MICAD))
Gadolinium based
contrast agents-
Magnevist, Dotarem,
Prohance, Gadovist,
Optimark, Eovist,
Vasovist/Ablavar.
Tm3+,
23
C
,
29
F
,
,
Manganese ferrite,
Iron oxides
99mTc
186Re, 188Re
111In, 123I, 125I,
131I,
170Tm, 177Lu,
Iodine contrast
agents-highlights
blood vessels as
well as tissues of
various organs
Barium-images
of the abdomen
and pelvis
Gastrogran
Microbubbles/
nanobubbles
Optison microbubbles-
per
uoropropane gas
encapsulated by a
serum albumin shell
Dyes and Glod
Physiology
5-Carboxy-uorescein,
uorescein, FITC, Alexa
Fluor 488 and 647, 680,
750, Oregon Green 488
Cy5, Cy5.5 Cy7
Rhodamin X, Rhodamin
Green, Luciferin, GFP
IR-783, IR-786,
IRDye78, IRDye800CW
NIR2, Quantum dot,
Single walled carbon
nanotubes, Ln based
molecular dyes
Technetium-99m: used mostly
for bone and heart scans
28
F-uoromisonidazole/
64
Cu-
ATSM-identiy hypoxia in
tissues,
gallium-attaches to area of
inammation
28
F-
uoride-imaging of new
bone formation
28
F-uorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
images the metabolic activity
of tissues. Can identify
cancerous cells.
Anatomy
Key use
Visualisation of cell
structures
Anatomical imaging
and functional
imaging of brain
activity-fMRI
Metabolic imaging
Lung and bone
tumour imaging
Va scular imaging
tABle 1.4
comparison of the different Imaging Modalities