Chemistry Reference
In-Depth Information
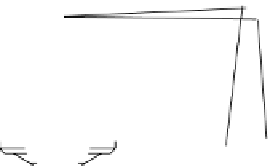
Point of light source
*
Brightly illuminated
point in sample
Illumination light path
Collection light path
Detector
Pinhole
In-focus rays
Out-of-focus rays
Objective lens
Focal plane
Cell on coverslip
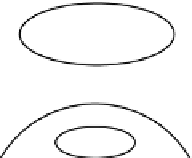
FIgure 1.21
The light path in a confocal microscope.
tABle 1.3
different types of optical Imaging Methods.
Imaging Methods
Maximum Depth
Target
Time
Primary Small Animal Use
clinical Potential
confocal microscopy
300 um
Physiological,
Molecular
Sec/Min
Gene expression, reporter
enzyme targeting, high
sensitivity, and use in
quantitative translational
research
Experimental
two-photon
microscopy
800 um
Physiological,
Molecular
Sec/Min
Gene expression imaging,
multiple probes
simultaneously
Experimental
Fluorescence
reflectance
imaging
5-7 mm
Physiological,
Molecular
Sec/Min
Gene expression activatable,
detects fluorochromes in
live and dead cells
Ye s
diffuse optical
tomography
15-20 mm
Physiological,
Molecular
Sec
Ye s
Fluorescence
molecular
tomography
0-15 cm
Physiological,
Molecular
Sec
Quantitative imaging of
targeted fluorochrome
reporters in deep tissues
no
Bioluminescence
imaging
2-3 cm
Molecular
Min
Gene expression, cell
tracking, quick and easy
Experimental