Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
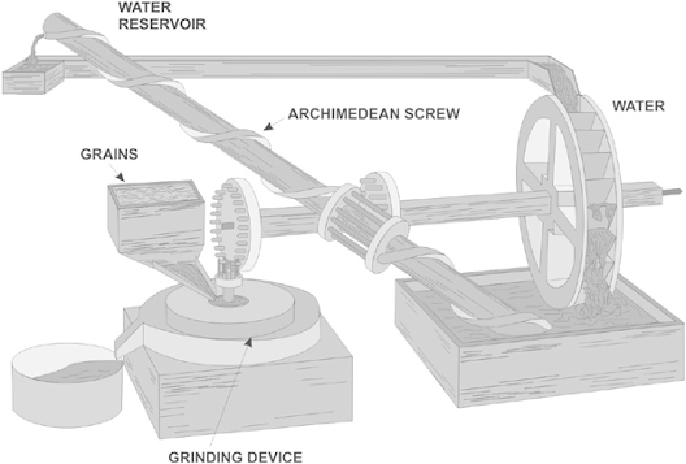
Figure 1.1 Fludd's “perpetuum mobile” machine
The law of conservation of mechanical energy can be extended to include thermal
phenomena. In an isolated system the sum of the mechanical and thermal energies
is conserved. This is the First Law of Thermodynamics, which states that the total
variation of energy contained in a closed system is equal to the (net) effect of the
heat and work the system undergoes with the environment. In other words, energy
can neither be created nor destroyed, an example of which is work performed by
gravitational forces.
The First Law can be extended to include all forms of energy: mechanical,
thermal, electrical, magnetic, chemical, and nuclear.