Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
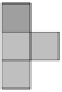
F
Forest
B
Burning forest
Burned forest
Watered forest
Figure 6.4:
The example scenario uses a 2-dimensional environment
with five different cell types (empty, forest, burning, burned,
watered). Two agents are present: a fireman (F) and a fire-
bug (B).
6.4 Macro-level modeling
The macro-level of the GRAMS reference model deals with all aspects
concerning integration of entities into a common environment and
interaction of multiple entities.
6.4.1 Simulation time
The
simulation time
T
is defined as totally ordered set of points
in time (i. e., antisymmetry, transitivity and totality are fulfilled),
cp. [151, p. 99f.], [36, p. 28]. The definition of simulation time in this
generality imposes the least constraints on the further modeling of
agent behavior and event handling.
Depending on the actual application, simulation time may be defined
in a
bottom-up
fashion, first defining simulation time on the micro-level
and subsequently deriving the simulation time on the macro-level as a
superset of all locally used simulation times. This allows developers of
different parts of a simulation model (e. g., different kinds of agents)
to use simulation times which are best-suited in their specific case.
The opposite approach is to define simulation time in
top-down
manner. In this case, simulation time is defined on the macro-level
first, and all entities on the micro-level have to use a subset of this
simulation time. The strict compliance of simulation time used on