Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
GRAMS reference model
Define basic building blocks
of agent-based models
Problem-specific conceptual models
CM
1
«i ns tantiation»
CM
2
...
«i mpl ementation»
Problem-specific executable models
EM
1
EM
2
...
«execution»
Define constraints for
simulation of a model
«constraints»
Simulation engine
(application)
«pa rtition»
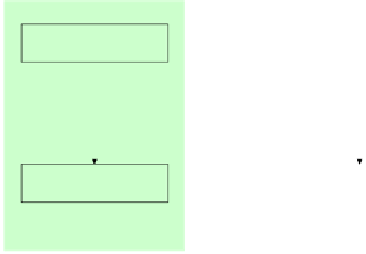
Model partitioning
Multiple strategies possible
Partitioned problem-specific
executable model EM
1
Model
partition 1
Model
partition 2
. . .
«execution»
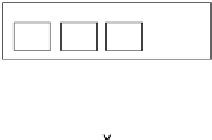
Parallel execution
Cluster-level
1 computer cluster - multiple nodes
Node 1
Node 2
. . .
Node-level
1 node - multiple processors
Processor 1.1
Processor 1.2
. . .
Processor-level
1 processor - multiple cores
Core 1.1.1
Core 1.1.2
. . .
Figure 8.1:
Model partitioning and multi-level parallelization.
Partitioning on macro-level
As the environment is a central element of agent-based models, the
environment has to be considered carefully for each partitioning
strategy. This is especially true, if multiple computing nodes can be
utilized. Two basic alternatives are
partitioning
the environment or
replicating
the environment. Partitioning the environment requires
that the environment is split up and distributed onto the available
computing nodes. Replicating the environment requires that the
environment is replicated on all computing nodes and only agents
or actions are distributed onto the available nodes.
Partitioning on micro-level
Partitioning on micro-level mainly concerns the decomposition of
the set of agents. Two different approaches can easily be devised: