Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
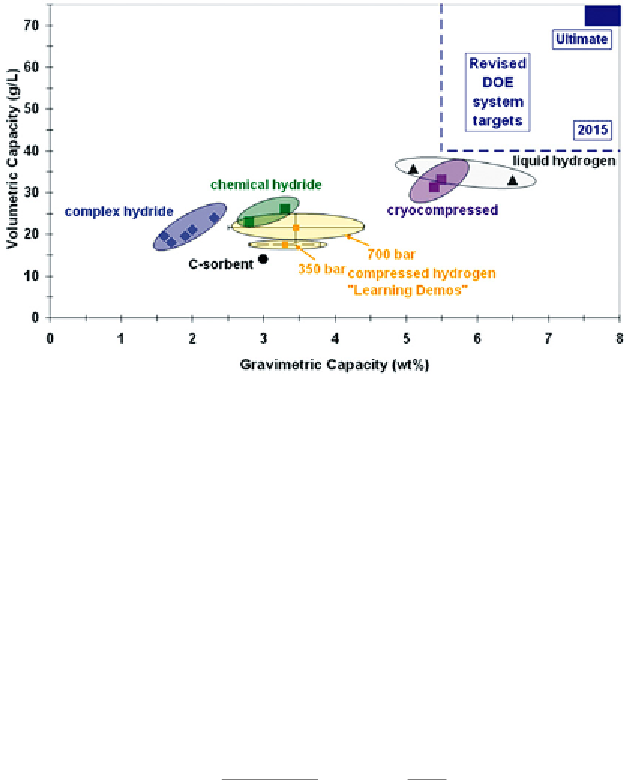
FIGURE 5.1
A summary of current status of hydrogen storage technologies in terms of weight, volume,
and cost. These values are estimates from storage system developers and the R&D community and will
be continuously updated by DOE as new technological advancements take place.
Source
: Reproduced
with permission from http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/storage/tech_status.html [2].
(See color insert.)
5.2 HIGH PRESSURE COMPRESSION
A common and simple method for storing and transporting hydrogen is to
compress hydrogen into a fixed volume (in a metal cylinder or tank) at high
pressure, so that the mass density of hydrogen will be increased. If under
high pressure
P
, the mass of compressed hydrogen is
m
H
, the tank volume
and mass are
V
tank
and
m
tank
, the effective gravimetric and volumetric capaci-
ties are
m
m
V
′
=
H
′
=
H
ρ
and
ρ
.
M
V
m
+
m
H
tank
tank
The parameters
P
,
V
tank
, and
m
H
are linked by the equation of state of
hydrogen,
f
(
P
,
V
tank
,
T
) = 0. The simplest approximation is the law of an
ideal gas,
PV
tank
=
nRT
.
(5.6)
where
m
M
H
n
=
,
Search WWH ::

Custom Search