Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1
15 bar
0.9
5 bar
1 bar
0.8
NH
3
1 bar
0.7
H
2
0.6
5 bar
0.5
15 bar
0.4
0.3
N
2
1 bar
0.2
5 bar
0.1
15 bar
0
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
1100
1200
1300
Temperature (K)
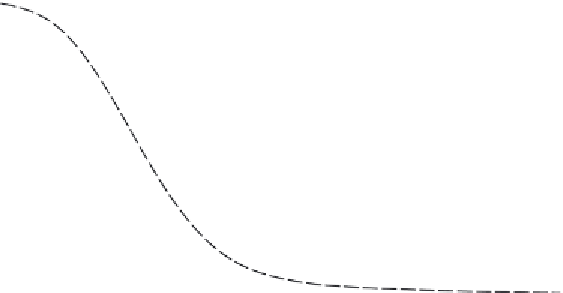
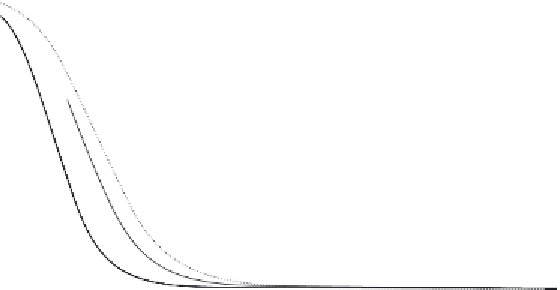
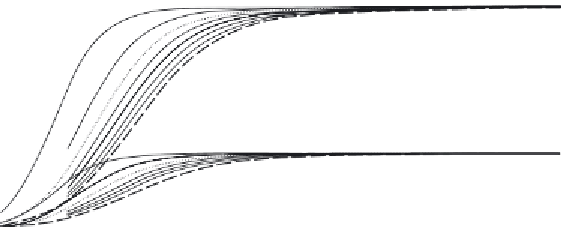
FIGURE 2.7
Chemical equilibrium of 2NH
3
= N
2
+ 3 H
2
as a function of temperature and pressure.
Source
: Reproduced with permission from Hacker and Kordesch [15].
which is exothermic thermodynamically but is only effective under pressure
and high temperature and with catalysts due to high kinetic barriers. Also,
ammonia cannot be simply released since it is hazardous. Thus, it is not easy
to use the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen as a direct means for
energy generation as in the case of hydrogen reaction with oxygen. However,
if ammonia can be produced at a low cost, it is a potential source for hydro-
gen, which is a promising energy carrier.
One major driving force for ammonia synthesis is nitrogen fixation for
producing fertilizers. There are a number of large-scale ammonia production
plants worldwide, producing a total of 131 million tons of ammonia in 2010
and projected to reach near 200 million tons by 2012. Hydrogen is used for
ammonia synthesis and is mainly produced from natural gas or other lique-
fied petroleum gases such as propane or butane, or petroleum naphtha. Figure
2.8 shows a flow chart of typical options for producing and purifying ammonia
synthesis gas.
The first step in the process is to remove sulfur compounds from the
feedstock because sulfur deactivates the catalysts used in subsequent steps.
Sulfur removal requires catalytic hydrogenation to convert sulfur compounds
to gaseous hydrogen sulfide, which is then absorbed and removed by passing
through beds of ZnO, where it is converted to solid zinc sulfide. The second
step is catalytic steam reforming of the sulfur-free feedstock to form hydro-
gen plus carbon monoxide. The third step uses catalytic shift conversion to
convert the carbon monoxide (reacting with H
2
O) to carbon dioxide (which






Search WWH ::

Custom Search