Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
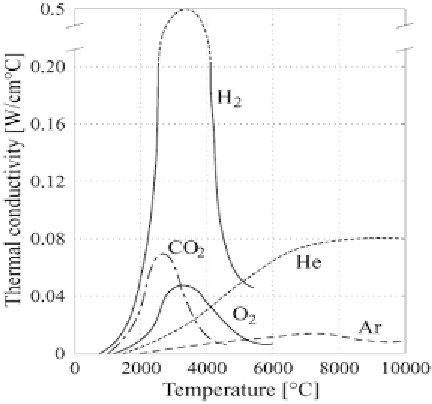
FIGURE 10.10
Thermal conductivity of various gases measured at different temperatures.
Source
:
Reproduced with permission from Suban et al. [18].
density, and therefore low viscosity, which allows it to be used as high per-
formance gaseous coolant. For example, hydrogen is commonly used in
power stations as a coolant in turbo generators, which are designed to provide
a low drag atmosphere and cooling for single-shaft and combined-cycle
applications in combination with steam turbines [20]. In addition, there was
attempt to use hydrogen as cooling gas in airplanes due to its low density.
For example, Algarni et al. compared the performance of liquid hydrogen
with methane as coolant for airplane [21]. The results suggested that liquid
hydrogen is a superior candidate for coolant since it saves 10% of the initial
total mass as compared with methane. Likewise, Ahmed et al. reported a
comparative study for cooling an aerospace plane using liquid hydrogen,
ammonia, and krypton [22]. They found that the required amount of liquid
hydrogen is less than that of liquid NH
3
or Kr, and thus proved that liquid
hydrogen is a better coolant. It should be noted that hydrogen is a highly
flammable gas, and therefore any cooling system using hydrogen coolant
should be completely sealed in order to guarantee only hydrogen gas is pre-
sented in the system to avoid explosion.
Liquid hydrogen is also a good coolant for superconductors, which will
be discussed in Section 10.6.2.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search